Transglutaminase 2 inhibition ameliorates cardiac fibrosis in myocardial infarction by inducing M2 macrophage polarization in vitro and in vivo
- PMID: 39737120
- PMCID: PMC11683372
- DOI: 10.25259/Cytojournal_32_2024
Transglutaminase 2 inhibition ameliorates cardiac fibrosis in myocardial infarction by inducing M2 macrophage polarization in vitro and in vivo
Abstract
Objective: Macrophages perform vital functions in cardiac remodeling after myocardial infarction (MI). Transglutaminase 2 (TG2) participates in fibrosis. Nevertheless, the role of TG2 in MI and mechanisms underlying macrophage polarization are unclear. This study aimed to discover the functions and possible mechanisms of TG2 in MI.
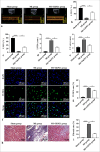
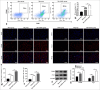
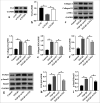
Material and methods: C57BL/6 mice were classified into three groups (six mice per group): Sham, MI, and MI+GK921 groups. GK921 acts as a TG2 inhibitor. Cardiac function, myocardial cell apoptosis, fibrosis, and macrophage phenotype in mouse experiments were detected through echocardiography, terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling, Masson staining, immunofluorescence, and flow cytometry, respectively. The in vitro study involved the treatment of mouse cardiac fibroblasts isolated from mice with transforming growth factor β1 (TGF-β1) and evaluation of fibrosis through the detection of the expressions of fibrosis-associated proteins using Western blot. Bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs) obtained from mice were triggered by interleukin (IL)-4, and the type of macrophages was determined through flow cytometry.
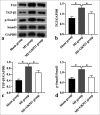
Results: In in vivo experiments, GK921 substantially improved cardiac injury and fibrosis, induced M2 macrophage polarization, and suppressed the TGF-β1/small mother against decapentaplegic 3 (Smad3) pathway in MI mice. Moreover, TG2 knockdown considerably decreased the expressions of fibrosis-associated proteins in TGF-β1-triggered mouse cardiac fibroblasts, which indicates the repressive effect of TG2 knockdown on fibrosis. In addition, the inhibition effect of TG2 downregulation on the TGF-β1/Smad3 pathway was proven in TGF-β1-treated mouse cardiac fibroblasts in vitro. Moreover, TG2 inhibition remarkably increased M2 macrophage polarization in IL-4-induced BMDMs.
Conclusion: TG2 inhibition facilitated M2 macrophage polarization to provide protection against MI-caused cardiac fibrosis in mice, and these effects may be attained through modulation of the TGF-β1/Smad3 pathway.
Keywords: Macrophage polarization; Myocardial infarction; Transforming growth factor β1/small mother against decapentaplegic 3 pathway; Transglutaminase 2.
© 2024 The Author(s). Published by Scientific Scholar.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Transglutaminase 2 mediates lung inflammation and remodeling by transforming growth factor beta 1 via alveolar macrophage modulation.Exp Lung Res. 2021 Dec;47(10):465-475. doi: 10.1080/01902148.2021.1998733. Epub 2021 Nov 24. Exp Lung Res. 2021. PMID: 34818962
-
Pirfenidone modulates macrophage polarization and ameliorates radiation-induced lung fibrosis by inhibiting the TGF-β1/Smad3 pathway.J Cell Mol Med. 2021 Sep;25(18):8662-8675. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16821. Epub 2021 Jul 29. J Cell Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 34327818 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomes from adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate cardiac damage after myocardial infarction by activating S1P/SK1/S1PR1 signaling and promoting macrophage M2 polarization.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2019 Sep;114:105564. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2019.105564. Epub 2019 Jul 2. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 31276786
-
Zerumbone, a humulane sesquiterpene from Syringa pinnatifolia, attenuates cardiac fibrosis by inhibiting of the TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway after myocardial infarction in mice.Phytomedicine. 2022 Jun;100:154078. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154078. Epub 2022 Mar 31. Phytomedicine. 2022. PMID: 35405613
-
Notch3 Ameliorates Cardiac Fibrosis After Myocardial Infarction by Inhibiting the TGF-β1/Smad3 Pathway.Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2016 Oct;16(4):316-24. doi: 10.1007/s12012-015-9341-z. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2016. PMID: 26487518
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
