Oncogene 5'-3' exoribonuclease 2 enhances epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway to promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis in non-small-cell lung cancer
- PMID: 39737134
- PMCID: PMC11683367
- DOI: 10.25259/Cytojournal_49_2024
Oncogene 5'-3' exoribonuclease 2 enhances epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway to promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis in non-small-cell lung cancer
Abstract
Objective: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and metastasis are the primary causes of mortality in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). 5'-3' exoribonuclease 2 (XRN2) plays an important role in the process of tumor EMT. Thus, this investigation mainly aimed to clarify the precise molecular pathways through which XRN2 contributes to EMT and metastasis in NSCLC.
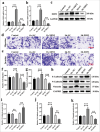
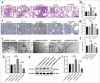
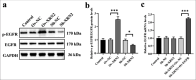
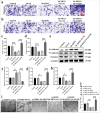
Material and methods: Western blot and quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction were first used to assess XRN2 levels in NSCLC cells. Subsequently, short hairpin RNA-XRN2 (Sh-XRN2) and XRN2 overexpression (Ov-XRN2) plasmids were transfected to NSCLC cells. The effects of Sh-XRN2 and Ov-XRN2 on NSCLC cell migration and invasion were evaluated by Transwell assay. Western blot experiments were conducted to assess the effects of Sh-XRN2 and Ov-XRN2 on proteins related to EMT and the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) signaling pathway in H460 cells. Then, Sh-XRN2 and EGFR overexpression (Ov-EGFR) plasmids were transfected to NSCLC cells. Changes in NSCLC cell migration and invasion were measured using a Transwell assay with Sh-XRN2 and Sh-XRN2+Ov-EGFR. Changes in the expression of proteins related to EMT in NSCLC cells were detected by Western blot assays with Sh-XRN2 and Sh-XRN2+Ov-EGFR. Furthermore, a subcutaneous tumor model for NSCLC was established. Immunohistochemical analysis was performed to assess the levels of Cluster of Differentiation 31 (CD31) in lung metastatic lesions. H460 cells transfected with Sh-XRN2, Ov-XRN2 or Sh-XRN2+Ov-EGFR were co-cultured with human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) to assess the tube formation ability of the cells.
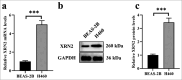
Results: Compared with those observed in human bronchial epithelial cells (BEAS-2B cells), XRN2 expression levels were significantly upregulated in NSCLC cell lines (H460 cells) (P < 0.001). XRN2 overexpression considerably promoted the NSCLC cell migration and invasion, EMT process, and tube formation ability of HUVECs (P < 0.001). On the contrary, XRN2 knockdown led to a reduction in these processes. In addition, XRN2 overexpression increased the expression levels of CD31 in lung metastatic lesions and activated the phosphorylation of EGFR signaling pathway (P < 0.001). Furthermore, Sh-XRN2+Ov-EGFR significantly promoted migration, invasion, and EMT processes in H460 cells (P < 0.001). In the meantime, compared with the co-H460+Sh-XRN2+Ov-NC group, co-H460+Sh-XRN2+Ov-EGFR significantly enhanced the tube formation ability of HUVECs (P < 0.001).
Conclusion: XRN2 promoted EMT and metastasis in NSCLC through improving the phosphorylation of the EGFR signaling pathway in NSCLC cells.
Keywords: 5’-3’ exoribonuclease 2; epidermal growth factor receptor; epithelial– mesenchymal transition; metastasis; non-small-cell lung cancer.
© 2024 The Author(s). Published by Scientific Scholar.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Chen B, Song Y, Zhan Y, Zhou S, Ke J, Ao W, et al. Fangchinoline inhibits non-small cell lung cancer metastasis by reversing epithelial-mesenchymal transition and suppressing the cytosolic ROS-related Akt-mTOR signaling pathway. Cancer Lett. 2022;543:215783. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2022.215783. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wang Y, Liu F, Chen L, Fang C, Li S, Yuan S, et al. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps (NETs) promote non-small cell lung cancer metastasis by suppressing lncRNA MIR503HG to activate the NF-kB/NLRP3 inflammasome pathway. Front Immunol. 2022;13:867516. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.867516. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
