Crispr-Cas9-based long non-coding RNA interference and activation identified that the aberrant expression of Myc-regulated ST8SIA6 antisense RNA 1 promotes tumorigenesis and metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 39737136
- PMCID: PMC11683396
- DOI: 10.25259/Cytojournal_109_2024
Crispr-Cas9-based long non-coding RNA interference and activation identified that the aberrant expression of Myc-regulated ST8SIA6 antisense RNA 1 promotes tumorigenesis and metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Objective: Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) participate in the formation, progression, and metastasis of cancer. This study aimed to explore the roles of the lncRNA ST8SIA6 antisense RNA 1 (ST8SIA6-AS1) in tumorigenesis and elucidate the underlying molecular mechanism of its upregulation in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Material and methods: A total of 56 in-house pairs of HCC tissues were examined, and ST8SIA6-AS1 levels were determined through real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR). The biological behavior of ST8SIA6-AS1 by Crispr-Cas9-based gene repression and activation was determined in vitro and in vivo. The binding sites and biological behavior of Myc proto-oncogene and forkhead box A on chromatin were investigated through luciferase reporter assays, chromatin immunoprecipitation-quantitative PCR, and co-immunoprecipitation (co-IP) assays. The regulatory mechanisms of ST8SIA6-AS1 expression were analyzed with encyclopedia of DNA elements and gene expression profiling interactive analysis.
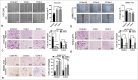
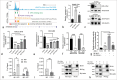
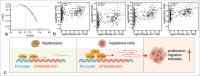
Results: The expression of ST8SIA6-AS1 significantly increased in multiple HCC cell lines and the 56 in-house pairs of HCC tissues (P = 0.0018). Functionally, high-efficiency Crispr-Cas9-based knockdown of ST8SIA6-AS1 revealed that ST8SIA6-AS1 knockdown attenuated the proliferation, migration, and infiltration of HCC cells and considerably reduced the growth rate of subcutaneous and orthotopic HCC tumors. Conversely, ST8SIA6-AS1 overexpression considerably improved the oncogenic characteristics of the HCC cells. Furthermore, ST8SIA6-AS1 upregulation was regulated by the direct binding of transcription factor Myc to the -260 bp to+155 bp and +1003 bp to +1312 bp regions of the ST8SIA6-AS1 transcription start site, which is a segment with high level of H3K27 acetylation. Myc knockdown or treatment with the BET bromodomain inhibitor JQ-1 considerably reduced ST8SIA6-AS1 RNA expression in the HCC cells.
Conclusion: Our study has established the oncogenic role of ST8SIA6-AS1 and elucidated the Myc-dependent upregulation mechanism of ST8SIA6-AS1 in HCC, providing a profound theoretical molecular basis for the carcinogenic function of ST8SIA6-AS1 in HCC.
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma; Long non-coding RNA; Myc proto-oncogene; ST8SIA6 antisense RNA 1; Tumorigenesis.
© 2024 The Author(s). Published by Scientific Scholar.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
ST8SIA6-AS1 promotes the development of hepatocellular carcinoma cells through miR-338-3p/NONO Axis.Dig Liver Dis. 2021 Sep;53(9):1192-1200. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2021.02.012. Epub 2021 Mar 12. Dig Liver Dis. 2021. PMID: 33722502
-
ST8SIA6-AS1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma by absorbing miR-5195-3p to regulate HOXB6.Cancer Biol Ther. 2020 Jul 2;21(7):647-655. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2020.1743150. Epub 2020 May 18. Cancer Biol Ther. 2020. PMID: 32420798 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA ST8SIA6-AS1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by regulating MAGEA3 and DCAF4L2 expression.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020 Dec 17;533(4):1039-1047. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.09.115. Epub 2020 Oct 1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020. PMID: 33012505
-
LncRNA ST8SIA6-AS1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation and resistance to apoptosis by targeting miR-4656/HDAC11 axis.Cancer Cell Int. 2020 Jun 11;20:232. doi: 10.1186/s12935-020-01325-5. eCollection 2020. Cancer Cell Int. 2020. PMID: 32536820 Free PMC article.
-
ST8SIA6-AS1, a novel lncRNA star in liver cancer.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Aug 15;12:1435664. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1435664. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 39211393 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Long non-coding RNAs and autophagy: dual drivers of Hepatocellular carcinoma progression.Cell Death Discov. 2025 Aug 11;11(1):376. doi: 10.1038/s41420-025-02667-7. Cell Death Discov. 2025. PMID: 40789840 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
