Analysis of the International Index of Erectile Function: psychometric evidence and measurement invariance across relationship status and age generations in a Chilean sample
- PMID: 39737143
- PMCID: PMC11683729
- DOI: 10.1093/sexmed/qfae084
Analysis of the International Index of Erectile Function: psychometric evidence and measurement invariance across relationship status and age generations in a Chilean sample
Abstract
Background: The International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF) stands out for its utility and widespread use to measure sexual function in men. However, it lacks consistency in its internal latent structure across studies, has not been evaluated for measurement invariance, and has not undergone psychometric validation for its 15-item form in Spanish among South American countries.
Aim: To examine the IIEF's psychometric evidence (ie, structural/criterion validity and reliability) in a sample of adult men and determine its measurement invariance across relationship status (single vs in a relationship) and age generations (generations Z, Y/millennials, and X).
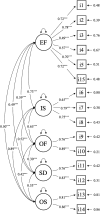
Methods: A sample of 650 sexually active males was derived from a broader Chilean study (Chilean Sex and Sexuality Study). We used a confirmatory factor analysis to determine the IIEF's structural validity, sexual satisfaction dimensions to establish its criterion-related validity, and Cronbach alpha and McDonald omega to assess the reliability of its scores.
Outcomes: Measures of goodness of fit.
Results: The evidence supported the 5-factor latent solution. Meanwhile, criterion-related validity revealed subtle yet significant differences in sexual satisfaction, with younger men displaying higher satisfaction in various sexual domains. In contrast, middle-aged men and those in a relationship showed better sexual function. Finally, the IIEF was invariant across age groups and relationship status at the factor covariance level.
Clinical translation: This study provides evidence that the IIEF is a valid, reliable, and invariant tool for the clinical practice in men's sexual health, particularly that associated with their sexual function and dysfunction.
Strengths and limitations: The study included a comprehensive validity analysis of the IIEF's psychometric properties, demonstrating its reliability and validity across diverse Chilean male subpopulations. The study also offered the IIEF's first assessment of measurement invariance and confirmed its suitability for clinical and research use in the Chilean population. Meanwhile, the study's limitations include a lack of clinical population and a sample predominantly younger, cisgender, and heterosexual.
Conclusion: Our study provides evidence of the IIEF's 5-factor structure and measurement invariance across age generations and relationship status in Chilean men, supporting its validity for clinical use and research and broadening its applicability in global sexual health studies, particularly in the Spanish-speaking South American male population.
Keywords: CSSS; Chile; erectile dysfunction; measurement invariance; psychometrics; sexual satisfaction.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of The International Society for Sexual Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Analysis of the psychometric evidence of the Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI) & measurement invariance across relationship status & age generations in a Chilean sample.Sex Med. 2025 Mar 4;13(1):qfaf010. doi: 10.1093/sexmed/qfaf010. eCollection 2025 Feb. Sex Med. 2025. PMID: 40041304 Free PMC article.
-
Psychometric Properties of Common Measures of Hypersexuality in an Online Canadian Sample.J Sex Med. 2022 Feb;19(2):331-346. doi: 10.1016/j.jsxm.2021.12.002. Epub 2022 Jan 3. J Sex Med. 2022. PMID: 34987002
-
Psychometric evaluation and measurement invariance of the Sexual and Relationship Distress Scale in cancer and nonclinical general reproductive-age populations.Sex Med. 2025 Jun 2;13(3):qfaf041. doi: 10.1093/sexmed/qfaf041. eCollection 2025 Jun. Sex Med. 2025. PMID: 40463813 Free PMC article.
-
The International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF)-A Systematic Review of Measurement Properties.J Sex Med. 2019 Jul;16(7):1078-1091. doi: 10.1016/j.jsxm.2019.04.010. Epub 2019 May 27. J Sex Med. 2019. PMID: 31147249
-
The Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI)-A Systematic Review of Measurement Properties.J Sex Med. 2019 May;16(5):640-660. doi: 10.1016/j.jsxm.2019.03.001. Epub 2019 Apr 5. J Sex Med. 2019. PMID: 30956110
Cited by
-
Analysis of the psychometric evidence of the Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI) & measurement invariance across relationship status & age generations in a Chilean sample.Sex Med. 2025 Mar 4;13(1):qfaf010. doi: 10.1093/sexmed/qfaf010. eCollection 2025 Feb. Sex Med. 2025. PMID: 40041304 Free PMC article.
-
The Multifaceted Impact of the SARS-CoV-2 Pandemic on Sexual Health, Function, and Behaviors: Implications for Public Health: A Scoping Review.Healthcare (Basel). 2025 Mar 5;13(5):559. doi: 10.3390/healthcare13050559. Healthcare (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40077121 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fielder R. Sexual functioning. In: Gellman MD, Turner JR, eds. Encyclopedia of Behavioral Medicine. Springer; 2013:1774–1777.
-
- American Psychiatric Publishing. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders: DSM-5. 5th ed. American Psychiatric Publishing; 2013.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources