The immune mechanisms of acute exacerbations of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- PMID: 39737178
- PMCID: PMC11682984
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1450688
The immune mechanisms of acute exacerbations of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
Abstract
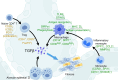
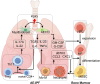
Acute exacerbations of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (AE-IPF) are the leading cause of mortality among patients with IPF. There is still a lack of effective treatments for AE-IPF, resulting in a hospitalization mortality rate as high as 70%-80%. To reveal the complicated mechanism of AE-IPF, more attention has been paid to its disturbed immune environment, as patients with IPF exhibit deficiencies in pathogen defense due to local immune dysregulation. During the development of AE-IPF, the classical stimulatory signals in adaptive immunity are inhibited, while the nonclassical immune reactions (Th17) are activated, attracting numerous neutrophils and monocytes to lung tissues. However, there is limited information about the specific changes in the immune response of AE-IPF. We summarized the immune mechanisms of AE-IPF in this review.
Keywords: Th17; acute exacerbations of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (AE-IPF); acute lung injury; immune mechanism; macrophages.
Copyright © 2024 Chen, Sun and Xu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
C-type lectin Mincle initiates IL-17-mediated inflammation in acute exacerbations of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 Mar;159:114253. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114253. Epub 2023 Jan 19. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 36680813
-
Clinical and economic burden of acute exacerbations of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: a prospective observational study in Spain (OASIS study).BMC Pulm Med. 2024 Jul 31;24(1):370. doi: 10.1186/s12890-024-03186-4. BMC Pulm Med. 2024. PMID: 39080648 Free PMC article.
-
Autoantibody-Targeted Treatments for Acute Exacerbations of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 17;10(6):e0127771. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0127771. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26083430 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Exacerbations in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis triggered by pulmonary and nonpulmonary surgery: a case series and comprehensive review of the literature.Lung. 2012 Aug;190(4):373-80. doi: 10.1007/s00408-012-9389-5. Epub 2012 Apr 29. Lung. 2012. PMID: 22543997 Review.
-
Animal models of acute exacerbation of pulmonary fibrosis.Respir Res. 2023 Nov 25;24(1):296. doi: 10.1186/s12931-023-02595-z. Respir Res. 2023. PMID: 38007420 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Collard HR, Ryerson CJ, Corte TJ, Jenkins G, Kondoh Y, Lederer DJ, et al. . Acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. An International Working Group Report. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. (2016) 194:265–75. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

