Fexuprazan safeguards the esophagus from hydrochloric acid-induced damage by suppressing NLRP1/Caspase-1/GSDMD pyroptotic pathway
- PMID: 39737189
- PMCID: PMC11682960
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1410904
Fexuprazan safeguards the esophagus from hydrochloric acid-induced damage by suppressing NLRP1/Caspase-1/GSDMD pyroptotic pathway
Abstract
Introduction: Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) and potassium-competitive acid blockers (P-CABs) are widely used to manage gastric acid-related disorders by inhibiting hydrochloric acid (HCl) secretion from parietal cells in the stomach. Although PPIs are known to have anti-inflammatory properties beyond their role in inhibiting gastric acid secretion, research on P-CABs is lacking. In this study, we aimed to investigate whether all available P-CABs exhibit anti-inflammatory effects in gastroesophageal reflux-induced esophagitis and to elucidate the underlying mechanisms.
Methods: Het-1A cells, normal esophageal epithelial cells, were treated with HCl (pH 4) for 30 min. Esomeprazole, a representative PPI, and three currently marketed P-CABs (vonoprazan, tegoprazan, and fexuprazan) were used for pretreatment. Total RNA sequencing was performed using Het-1A cells pretreated with 1% DMSO or fexuprazan, followed by exposure to HCl. Pyroptosis was measured using lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release and Annexin V-FITC/PI staining. Western blotting, qRT-PCR, and ELISA were used to determine the expression of the related genes.
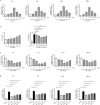
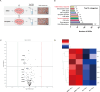
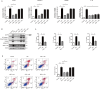
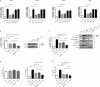
Results: Pretreatment with esomeprazole, vonoprazan, tegoprazan, and fexuprazan significantly inhibited the HCl-induced pro-inflammatory cytokines, including IL-6, IL-8, IL-1β, and TNF-α. Fexuprazan and vonoprazan significantly attenuated the HCl-induced pyroptosis rate, as assessed by elevated LDH release and Annexin V-FITC/PI staining, whereas esomeprazole and tegoprazan did not. RNA sequencing revealed that NOD-like receptor (NLR) family pyrin domain-containing 1 (NLRP1) was significantly reduced in Het-1A cells pretreated with fexuprazan compared to those treated with DMSO. Fexuprazan and vonoprazan markedly reduced the HCl-induced transcriptional and translational expression of genes involved in the pyroptosis pathway, including NLRP1, Caspase-1, gasdermin D, and IL-1β. Notably, fexuprazan reduced the HCl-induced increase in pyroptosis and IL-1β using siRNA, even in the presence of NLRP1 knockdown. Fexuprazan, tested on inflammatory THP-1 macrophage cells, significantly reduced NLRP1 expression and inhibited lipopolysaccharide-induced pyroptosis.
Conclusion: Our findings reveal that all p-CABs exhibit anti-inflammatory properties, while fexuprazan inhibits inflammation and pyroptosis of esophageal cells caused by the gastric acid. Therefore, it is presumed to have additional benefits in gastroesophageal reflux disease in addition to suppressing gastric acid secretion.
Keywords: NLRP1; P-CABs; esophagus; fexuprazan; hcl; pyroptosis.
Copyright © 2024 Kim, Yoon, Jung, Kim, Kim and Lee.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cytokine Secretion and Pyroptosis of Thyroid Follicular Cells Mediated by Enhanced NLRP3, NLRP1, NLRC4, and AIM2 Inflammasomes Are Associated With Autoimmune Thyroiditis.Front Immunol. 2018 Jun 4;9:1197. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01197. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29915579 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of amyloid β (Aβ)42 and Gasdermin D on the progression of Alzheimer's disease in vitro and in vivo through the regulation of astrocyte pyroptosis.Aging (Albany NY). 2023 Nov 2;15(21):12209-12224. doi: 10.18632/aging.205174. Epub 2023 Nov 2. Aging (Albany NY). 2023. PMID: 37921870 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of P-CABs in GERD.Am J Gastroenterol. 2025 May 1;120(5):993-998. doi: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000003140. Epub 2024 Oct 17. Am J Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 39466255 Review.
-
Safety of potassium-competitive acid blockers in the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease.Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2025 Jan;21(1):53-68. doi: 10.1080/17425255.2024.2397433. Epub 2024 Sep 24. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 39189409 Review.
-
Fexuprazan mitigates NSAID-induced small intestinal injury by restoring intestinal barrier integrity in mice.Biomed Pharmacother. 2025 Sep;190:118386. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2025.118386. Epub 2025 Aug 5. Biomed Pharmacother. 2025. PMID: 40753937
Cited by
-
Comparing Proton Pump Inhibitors and Emerging Acid-Suppressive Therapies in Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: A Systematic Review.Cureus. 2025 May 17;17(5):e84311. doi: 10.7759/cureus.84311. eCollection 2025 May. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40535413 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kim JS, Seo SI, Kang SH, Lee SK, Kim AR, Park HW, et al. . Effects of tegoprazan versus esomeprazole on nighttime heartburn and sleep quality in gastroesophageal reflux disease: a multicenter double-blind randomized controlled trial. J Neurogastroenterol Motility. (2023) 29:58. doi: 10.5056/jnm22104 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

