Impaired interhemispheric synchrony in patients with iridocyclitis and classification using machine learning: an fMRI study
- PMID: 39737192
- PMCID: PMC11683089
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1474988
Impaired interhemispheric synchrony in patients with iridocyclitis and classification using machine learning: an fMRI study
Abstract
Background: This study examined the interhemispheric integration function pattern in patients with iridocyclitis utilizing the voxel-mirrored homotopic connectivity (VMHC) technique. Additionally, we investigated the ability of VMHC results to distinguish patients with iridocyclitis from healthy controls (HCs), which may contribute to the development of objective biomarkers for early diagnosis and intervention in clinical set.
Methods: Twenty-six patients with iridocyclitis and twenty-six matched HCs, in terms of sex, age, and education level, underwent resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) examinations. The study employed the voxel-mirrored homotopic connectivity (VMHC) technique to evaluate interhemispheric integration functional connectivity indices at a voxel-wise level. The diagnostic efficacy of VMHC was evaluated using a support vector machine (SVM) classifier, with classifier performance assessed through permutation test analysis. Furthermore, correlation analyses was conducted to investigate the associations between mean VMHC values in various brain regions and clinical features.
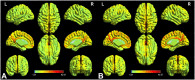
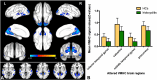
Results: Patients with iridocyclitis exhibited significantly reduced VMHC signal values in the bilateral inferior temporal gyrus, calcarine, middle temporal gyrus, and precuneus compared to HCs (voxel-level P < 0.01, Gaussian Random Field correction; cluster-level P < 0.05). Furthermore, the extracted resting-state zVMHC features effectively classified patients with iridocyclitis and HCs, achieving an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) of 0.74 and an overall accuracy of 0.673 (P < 0.001, non-parametric permutation test).
Conclusion: Our findings reveal disrupted interhemispheric functional organization in patients with iridocyclitis, offering insight into the pathophysiological mechanisms associated with vision loss and cognitive dysfunction in this patient population. This study also highlights the potential of machine learning in ophthalmology and the importance of establishing objective biomarkers to address diagnostic heterogeneity.
Keywords: fMRI; interhemispheric integration; iridocyclitis; machine learning; support vector machine.
Copyright © 2024 Tong, Wen and Huang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Altered Functional Connectivity of the Primary Visual Cortex in Patients With Iridocyclitis and Assessment of Its Predictive Value Using Machine Learning.Front Immunol. 2021 May 7;12:660554. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.660554. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34025659 Free PMC article.
-
Reduction of Interhemispheric Homotopic Connectivity in Cognitive and Visual Information Processing Pathways in Patients With Thyroid-Associated Ophthalmopathy.Front Hum Neurosci. 2022 Jun 30;16:882114. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2022.882114. eCollection 2022. Front Hum Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35865354 Free PMC article.
-
Disrupted interhemispheric functional connectivity in primary angle-closure glaucoma: a functional MRI study: voxel-mirrored homotopic connectivity in primary angle-closure glaucoma patients.Neuroreport. 2022 Oct 5;33(14):604-611. doi: 10.1097/WNR.0000000000001823. Epub 2022 Aug 26. Neuroreport. 2022. PMID: 36062513
-
Abnormal postcentral gyrus voxel-mirrored homotopic connectivity as a biomarker of mild cognitive impairment: A resting-state fMRI and support vector machine analysis.Exp Gerontol. 2024 Oct 1;195:112547. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2024.112547. Epub 2024 Aug 24. Exp Gerontol. 2024. PMID: 39168359
-
Alternations of interhemispheric functional connectivity in patients with optic neuritis using voxel-mirrored homotopic connectivity: A resting state fMRI study.Brain Imaging Behav. 2023 Feb;17(1):1-10. doi: 10.1007/s11682-022-00719-5. Epub 2022 Nov 28. Brain Imaging Behav. 2023. PMID: 36437427
References
-
- Jabs DA, Nussenblatt RB, Rosenbaum JT, Standardization of Uveitis Nomenclature (SUN) Working Group . Standardization of uveitis nomenclature for reporting clinical data. Results of the first international workshop. Am J Ophthalmology. (2005) 140:509–16. doi: 10.1016/j.ajo.2005.03.057 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

