The effect and application of adiponectin in hepatic fibrosis
- PMID: 39737222
- PMCID: PMC11683834
- DOI: 10.1093/gastro/goae108
The effect and application of adiponectin in hepatic fibrosis
Abstract
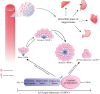
Hepatic fibrosis, a degenerative liver lesion, significantly contributes to the deterioration and mortality among patients with chronic liver diseases. The condition arises from various factors including toxins, such as alcohol, infections like different types of viral hepatitis, and metabolic diseases. Currently, there are no effective treatments available for liver fibrosis. Recent research has shown that adiponectin (ADPN) exhibits inhibitory effects on hepatic fibrosis. ADPN, an adipocytokine secreted by mature adipocytes, features receptors that are widely distributed across multiple tissues, especially the liver. In the liver, direct effects of ADPN on liver fibrosis include reducing inflammation and regulating hepatic stellate cell proliferation and migration. And its indirect effects include alleviating hepatic endoplasmic reticulum stress and reducing inflammation in hepatic lobules, thereby mitigating hepatic fibrosis. This review aims to elucidate the regulatory role of ADPN in liver fibrosis, explore how ADPN and its receptors alleviate endoplasmic reticulum stress, summarize ADPN detection methods, and discuss its potential as a novel marker and therapeutic agent in combating hepatic fibrosis.
Keywords: adiponectin; cirrhosis; endoplasmic reticulum stress; hepatic fibrosis; hepatic stellate cell.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press and Sixth Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have indicated they have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Devarbhavi H, Asrani SK, Arab JP. et al. Global burden of liver disease: 2023 update. J Hepatol 2023;79:516–37. - PubMed
-
- Zhao Q, Liang L, Zhai F. et al. A bibliometric and visualized analysis of liver fibrosis from 2002 to 2022. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2023;38:359–69. - PubMed
-
- Rowe IA. Lessons from epidemiology: the burden of liver disease. Dig Dis 2017;35:304–9. - PubMed
-
- She H, Xiong S, Hazra S. et al. Adipogenic transcriptional regulation of hepatic stellate cells. J Biol Chem 2005;280:4959–67. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

