Safety and durability of the immune response after vaccination with the heterologous schedule of anti-COVID-19 vaccines SOBERANA®02 and SOBERANA® Plus in children 3-18 years old
- PMID: 39737224
- PMCID: PMC11683288
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jvacx.2024.100595
Safety and durability of the immune response after vaccination with the heterologous schedule of anti-COVID-19 vaccines SOBERANA®02 and SOBERANA® Plus in children 3-18 years old
Abstract
Background: The heterologous three-dose schedule of the protein subunit anti-COVID-19 SOBERANA®02 and SOBERANA® Plus vaccines has proved its safety, immunogenicity and efficacy in pediatric population, but durability of immunogenicity is not yet dilucidated. This study reports the safety and durability of the humoral and cellular responses in children and adolescents 5-7 months after receiving the heterologous vaccine schedule of SOBERANA® 02 and SOBERANA® Plus.
Methods: Children participating in a phase I/II clinical trial were followed-up for 5-7 months after the last dose. They were clinically examined by medical doctors, and their parents were interviewed searching for long-term adverse events. Blood samples were collected to evaluate the duration of humoral and cellular immune responses. Sera were tested for the presence of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid (N) protein.
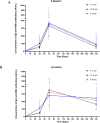
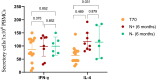
Results: There were no reports of severe adverse events such as coagulation disorders, myocarditis, or pericarditis. None of the participants who withdrew from the trial during the follow-up period did so due to post-vaccination adverse events. The humoral response waned in time for N-negative children, but levels of specific and neutralizing antibodies remained similar to those attained after the second dose of SOBERANA® 02 in the heterologous schedule. Neutralizing antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 D614G and omicron BA.1 were detected 5-7 months post-vaccination. RBD-specific IFN-γ secreting cells showed no significant change compared to levels following primary immunization, in both N-negative and N-positive children.
Conclusions: The vaccination regimen was safe over time, and both humoral and cellular immunity persisted in the vaccinated population aged 3-18 years, 5-7 months after receiving the heterologous SOBERANA® 02 and SOBERANA® Plus vaccine schedule.Trial registry: https://rpcec.sld.cu/trials/RPCEC00000374-En.
Keywords: COVID-19 vaccine; Cellular response; Conjugate vaccine; Pediatric vaccine; RBD; SARS-CoV-2; Subunit vaccine.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: The authors DGR, SFC, BPM, MRG, RPN, DSM, MMP, YCR, YVB, VVB declare to be employees at Finlay Vaccine Institute. The rest of the authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. No author received an honorarium for contributing to this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Safety and immunogenicity of anti-SARS CoV-2 vaccine SOBERANA 02 in homologous or heterologous scheme: Open label phase I and phase IIa clinical trials.Vaccine. 2022 Jul 29;40(31):4220-4230. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2022.05.082. Epub 2022 Jun 6. Vaccine. 2022. PMID: 35691871 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Safety and immunogenicity of anti-SARS-CoV-2 heterologous scheme with SOBERANA 02 and SOBERANA Plus vaccines: Phase IIb clinical trial in adults.Med. 2022 Nov 11;3(11):760-773.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.medj.2022.08.001. Epub 2022 Aug 8. Med. 2022. PMID: 35998623 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Real-world effectiveness of the heterologous SOBERANA-02 and SOBERANA-Plus vaccine scheme in 2-11 years-old children during the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron wave in Cuba: a longitudinal case-population study.Lancet Reg Health Am. 2024 Apr 23;34:100750. doi: 10.1016/j.lana.2024.100750. eCollection 2024 Jun. Lancet Reg Health Am. 2024. PMID: 38699214 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Immune Response after Vaccination with SOBERANA® 02 and SOBERANA® plus Heterologous Scheme and Natural Infection in Young Children.Vaccines (Basel). 2023 Oct 25;11(11):1636. doi: 10.3390/vaccines11111636. Vaccines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38005968 Free PMC article.
-
Open-label phase I/II clinical trial of SARS-CoV-2 receptor binding domain-tetanus toxoid conjugate vaccine (FINLAY-FR-2) in combination with receptor binding domain-protein vaccine (FINLAY-FR-1A) in children.Int J Infect Dis. 2023 Jan;126:164-173. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2022.11.016. Epub 2022 Nov 18. Int J Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 36403819 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- W.H.O WHO roadmap on uses of COVID-19 vaccines in the context of Omicron and high population immunity. https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/373987/WHO-2019-nCoV-Vaccine...
-
- Toledo-Romani M.E., et al. Real-world effectiveness of the heterologous SOBERANA-02 and SOBERANA-Plus vaccine scheme in 2–11 years-old children during the SARS-CoV-2 omicron wave in Cuba: a longitudinal case-population study. Lancet Regional Health – Americas. 2024;34 doi: 10.1016/j.lana.2024.100750. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

