Efficacy and Safety of Ultrasound-Guided Pulsed Radiofrequency Therapy of Stellate Ganglion on Refractory Painful Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
- PMID: 39737247
- PMCID: PMC11683198
- DOI: 10.2147/JPR.S497061
Efficacy and Safety of Ultrasound-Guided Pulsed Radiofrequency Therapy of Stellate Ganglion on Refractory Painful Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
Abstract
Background: The best tool for the management of pain associated with distal symmetric peripheral neuropathy (DSPN) is a matter of debate. Therefore, the study aimed to explore whether ultrasound-guided pulsed radiofrequency (PRF) therapy of the stellate ganglion (SG) in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients with painful DSPN could decrease pain severity and the need for analgesics.
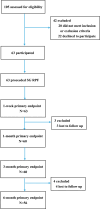
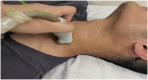
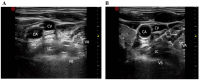
Methods: Fifty-six T2DM patients with refractory painful DSPN were enrolled in this study, who then received bilateral ultrasound-guided PRF therapy of SG. The patients completed visual analog scale (VAS), simplified McGill pain questionnaire (SF-MPQ), Toronto clinical score system (TCSS), sleep duration at night (SDN), pain disability index (PDI), Karnofsky performance status (KPS), and depression screening scale (PHQ-9). After procedures, the degree of perceived pain relief, numbness relief and chills relief of the patients, and side effects were assessed. All patients underwent evaluation after the last procedure at 1, 4, 12 and 24-week follow-up periods.
Results: The postoperative VAS, SF-MPQ, TCSS, PDI and PHQ-9 scores were significantly lower, while the KPS values higher than the preoperative (P<0.05). The postoperative SDN was longer than the preoperative (P<0.05). The degree of perceived pain relief, chills relief, and numbness relief at 4, 12, and 24 weeks were lower than that at 1 week after the procedures (P<0.05). The postoperative rates of administration of analgesic were lower than those of preoperative period (P<0.05). The significant effective rates at 1, 4, 12, and 24 weeks after the procedure were 67.86%, 42.86%, 21.43%, and 17.86% and the total effective rates were 89.29%, 71.43%, 46.43%, and 32.14%. No serious complication was observed.
Conclusion: Ultrasound-guided stellate ganglion PRF therapy can effectively relieve pain and improve the quality of life in T2DM patients with refractory painful DSPN.
Keywords: painful diabetic neuropathy; pulsed radiofrequency; stellate ganglion; type 2 diabetes mellitus.
© 2024 Wang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists. This paper has been uploaded to Research Square as a preprint: https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-3128530/v1.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

