The Impact of Headaches in Young Adults: An Analysis of Types, Triggers, and Daily Functioning Through the Headache-Attributed Restriction, Disability, Social Handicap, and Impaired Participation (HARDSHIP) Questionnaire
- PMID: 39737296
- PMCID: PMC11684540
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.74792
The Impact of Headaches in Young Adults: An Analysis of Types, Triggers, and Daily Functioning Through the Headache-Attributed Restriction, Disability, Social Handicap, and Impaired Participation (HARDSHIP) Questionnaire
Abstract
Background: Headaches affect people's social, intellectual, and personal lives and are quite common worldwide, especially among young adults. Primary headaches that cause significant impairment, such as tension-type headaches (TTH) and migraines, frequently start in adolescence and early adulthood. Research on the incidence and consequences of headache problems among young people in India is scarce, especially when it comes to a variety of academic fields.
Objectives: This study aims to 1) estimate the prevalence and types of headaches among young adults aged 18-24 years and 2) identify common triggers and assess the social and academic impact of headache disorders.
Methods: Young adults from different academic backgrounds in Chennai, South India, participated in this cross-sectional survey during September and October of 2024. A total of 438 participants across the Medical, Engineering, Dental, and Arts and Science disciplines were reached via snowball sampling. The study utilized a questionnaire based on Headache-Attributed Restriction, Disability, Social Handicap, and Impaired Participation to gather data on demographics, headache types, triggers, and their impact using Google Forms. Statistical Product and Service Solutions version 21 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY) was used for the statistical analysis, and associations were evaluated using the chi-square and analysis of variance tests.
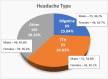
Results: The average age of the 438 participants was 20.1 years. Of the 438 respondents, 60.9% (267 subjects) reported having headaches in the last 12 months, with 54.6% reporting headaches in the last 30 days. Among those with headache disorders (267 subjects), 35% were diagnosed with TTH, 26% with migraine, and the remaining 39% had other types of headache. Compared with TTH and other headaches, migraines were linked to greater rates of academic interference, interruption of leisure activities, and absenteeism. In addition, migraineurs reported greater levels of social avoidance (46.3%) and a substantial family history (31.6%) compared to other headache disorders. The most often stated trigger was personal stress (38.7%), which was followed by academic stress, sinusitis, and sleep difficulties.
Conclusions: Headaches affect social life, everyday activities, and academic performance in young adults. They are highly prevalent and bothersome issues. More severe impairment seems to result from migraines than from TTH. To enhance the treatment of headache problems in this group, it is imperative to raise awareness, encourage early intervention, and remove obstacles to accessing healthcare.
Keywords: hardship; headache; headache impact; headache trigger; migraine; tension type of headache; young adults.
Copyright © 2024, Mahendran et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent for treatment and open access publication was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Saveetha Review Board issued approval 309/09/2024/Faculty/SRB/SMCH. Animal subjects: All authors have confirmed that this study did not involve animal subjects or tissue. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
References
-
- Migraine and other headache disorders. [ Oct; 2024 ];https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/headache-disorders 2024 3
-
- Global incidence, prevalence, years lived with disability (YLDs), disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs), and healthy life expectancy (HALE) for 371 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories and 811 subnational locations, 1990-2021: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. GBD 2021 Diseases and Injuries Collaborators. Lancet. 2024;403:2133–2161. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources