Cost Outcomes of Virtual Surgical Planning in Head and Neck Reconstruction: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 39737872
- PMCID: PMC11816551
- DOI: 10.1002/hed.28035
Cost Outcomes of Virtual Surgical Planning in Head and Neck Reconstruction: A Systematic Review
Abstract
Background: Virtual surgical planning (VSP) is an emerging method in head and neck reconstruction with demonstrated benefits, however, its economic viability is supported with mixed evidence.
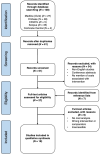
Methods: A structured search was performed in five electronic databases. Studies that performed an economic evaluation on VSP in head and neck reconstruction were included. Data regarding VSP workflow, costs, and variables influencing costs were recorded and synthesized.
Results: Eighteen studies met the final inclusion criteria (n = 733). Fourteen out of 18 studies (78%) found that VSP either generated cost savings or was comparable to freehand surgery (FHS). The majority of cost savings were generated from reduced OR times and LOS/LOH. In addition, greater cost savings were associated with in-house VSP workflows compared to those that are outsourced.
Conclusion: VSP is potentially cost-beneficial compared to traditional unplanned surgery, however, substantial heterogeneity amongst methods and outcome measures impedes the generalizability of these findings.
Trial registration: PROSPERO: CRD42024504398.
Keywords: cost savings; cost‐effectiveness; free flap reconstruction; maxillary reconstruction; virtual surgical planning.
© 2024 The Author(s). Head & Neck published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Urken M. L., Bridger A. G., Zur K. B., and Genden E. M., “The Scapular Osteofasciocutaneous Flap: A 12‐Year Experience,” Archives of Otolaryngology – Head & Neck Surgery 127, no. 7 (2001): 862–869. - PubMed
-
- Kearns M., Ermogenous P., Myers S., and Ghanem A. M., “Osteocutaneous Flaps for Head and Neck Reconstruction: A Focused Evaluation of Donor Site Morbidity and Patient Reported Outcome Measures in Different Reconstruction Options,” Archives of Plastic Surgery 45, no. 6 (2018): 495–503, 10.5999/aps.2017.01592. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous