MEGF9 prevents lipopolysaccharide-induced cardiac dysfunction through activating AMPK pathway
- PMID: 39737911
- PMCID: PMC11703103
- DOI: 10.1080/13510002.2024.2435252
MEGF9 prevents lipopolysaccharide-induced cardiac dysfunction through activating AMPK pathway
Abstract
Objective: Inflammation and oxidative damage play critical roles in the pathogenesis of sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction. Multiple EGF-like domains 9 (MEGF9) is essential for cell homeostasis; however, its role and mechanism in sepsis-induced cardiac injury and impairment remain unclear.
Methods: Adenoviral and adeno-associated viral vectors were applied to overexpress or knock down the expression of MEGF9 in vivo and in vitro. To stimulate septic injury, cardiomyocytes and mice were treated lipopolysaccharide (LPS). To clarify the necessity of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), global AMPK knockout mice were used.
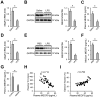
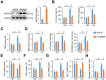
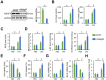
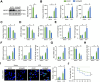
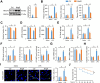
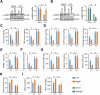
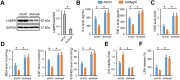
Results: We found that MEGF9 expressions were reduced in cardiomyocytes and mice by LPS stimulation. Compared with negative controls, plasma MEGF9 levels were also decreased in septic patients, and negatively correlated with LPS-induced cardiac dysfunction. In addition, MEGF9 overexpression attenuated, while MEGF9 knockdown aggravated LPS-induced inflammation and oxidative damage in vivo and in vitro, thereby regulating LPS-induced cardiac injury and impairment. Mechanistic studies revealed that MEGF9 overexpression alleviated LPS-induced cardiac dysfunction through activating AMPK pathway.
Conclusion: We for the first time demonstrate that MEGF9 prevents LPS-related inflammation, oxidative damage and cardiac injury through activating AMPK pathway, and provide a proof-of-concept for the treatment of LPS-induced cardiac dysfunction by targeting MEGF9.
Keywords: AMPK; LPS-induced cardiac dysfunction; inflammation; oxidative damage.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Oxycodone attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced myocardial injury by inhibiting inflammation, oxidation and pyroptosis via Nrf2/HO-1 signalling pathway.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2024 Sep;51(9):e13910. doi: 10.1111/1440-1681.13910. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39073215
-
The Protective Effects of Melatonin Against LPS-Induced Septic Myocardial Injury: A Potential Role of AMPK-Mediated Autophagy.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020 Apr 16;11:162. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2020.00162. eCollection 2020. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020. PMID: 32373063 Free PMC article.
-
Luteolin attenuates sepsis‑induced myocardial injury by enhancing autophagy in mice.Int J Mol Med. 2020 May;45(5):1477-1487. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2020.4536. Epub 2020 Mar 11. Int J Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32323750 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of AMP-activated protein kinase accentuates lipopolysaccharide-induced lung endothelial barrier dysfunction and lung injury in vivo.Am J Pathol. 2013 Mar;182(3):1021-30. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2012.11.022. Epub 2013 Jan 7. Am J Pathol. 2013. PMID: 23306156 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of the AMPK/Nrf2 pathway ameliorates LPS-induced acute lung injury by inhibiting oxidative stress and reducing inflammation.J Cardiothorac Surg. 2024 Oct 1;19(1):568. doi: 10.1186/s13019-024-03020-2. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2024. PMID: 39354500 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
miR-200c inhibition and catalase accelerate diabetic wound healing.J Biomed Sci. 2025 Feb 14;32(1):21. doi: 10.1186/s12929-024-01113-7. J Biomed Sci. 2025. PMID: 39948670 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
