A microbiota-derived metabolite, 3-phenyllactic acid, prolongs healthspan by enhancing mitochondrial function and stress resilience via SKN-1/ATFS-1 in C. elegans
- PMID: 39737960
- PMCID: PMC11686233
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-55015-1
A microbiota-derived metabolite, 3-phenyllactic acid, prolongs healthspan by enhancing mitochondrial function and stress resilience via SKN-1/ATFS-1 in C. elegans
Abstract
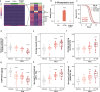
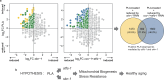
The mechanisms underlying the impact of probiotic supplementation on health remain largely elusive. While previous studies primarily focus on the discovery of novel bioactive bacteria and alterations in the microbiome environment to explain potential probiotic effects, our research delves into the role of living Lactiplantibacillus (formerly known as Lactobacillus) and their conditioned media, highlighting that only the former, not dead bacteria, enhance the healthspan of Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans). To elucidate the underlying mechanisms, we conduct transcriptomic profiling through RNA-seq analysis in C. elegans exposed to GTB1, a strain of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum or 3-phenyllactic acid (PLA), mimicking the presence of key candidate metabolites of GTB1 and evaluating healthspan. Our findings reveal that PLA treatment significantly extends the healthspan of C. elegans by promoting energy metabolism and stress resilience in a SKN-1/ATFS-1-dependent manner. Moreover, PLA-mediated longevity is associated with a novel age-related parameter, the Healthy Aging Index (HAI), introduced in this study, which comprises healthspan-related factors such as motility, oxygen consumption rate (OCR), and ATP levels. Extending the relevance of our work to humans, we observe an inverse correlation between blood PLA levels and physical performance in patients with sarcopenia, when compared to age-matched non-sarcopenic controls. Our investigation thus sheds light on the pivotal role of the metabolite PLA in probiotics-mediated enhancement of organismal healthspan, and also hints at its potential involvement in age-associated sarcopenia. These findings warrant further investigation to delineate PLA's role in mitigating age-related declines in healthspan and resilience to external stressors.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Gimeno-Mallench, L. et al. The relationship between diet and frailty in aging. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets20, 1373–1382 (2020). - PubMed
-
- Li, W. et al. Antioxidant properties of lactic acid bacteria isolated from traditional fermented yak milk and their probiotic effects on the oxidative senescence of Caenorhabditis elegans. Food Funct.13, 3690–3703 (2022). - PubMed
-
- Liu, G. et al. Lactic acid bacteria feeding reversed the malformed eye structures and ameliorated gut microbiota profiles of Drosophila melanogaster Alzheimer’s disease model. J. Appl. Microbiol.132, 3155–3167 (2022). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

