Neuromorphic-enabled video-activated cell sorting
- PMID: 39737963
- PMCID: PMC11685671
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-55094-0
Neuromorphic-enabled video-activated cell sorting
Abstract
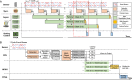
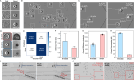
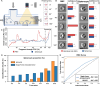
Imaging flow cytometry allows image-activated cell sorting (IACS) with enhanced feature dimensions in cellular morphology, structure, and composition. However, existing IACS frameworks suffer from the challenges of 3D information loss and processing latency dilemma in real-time sorting operation. Herein, we establish a neuromorphic-enabled video-activated cell sorter (NEVACS) framework, designed to achieve high-dimensional spatiotemporal characterization content alongside high-throughput sorting of particles in wide field of view. NEVACS adopts event camera, CPU, spiking neural networks deployed on a neuromorphic chip, and achieves sorting throughput of 1000 cells/s with relatively economic hybrid hardware solution (~$10 K for control) and simple-to-make-and-use microfluidic infrastructures. Particularly, the application of NEVACS in classifying regular red blood cells and blood-disease-relevant spherocytes highlights the accuracy of using video over a single frame (i.e., average error of 0.99% vs 19.93%), indicating NEVACS' potential in cell morphology screening and disease diagnosis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Spark-generated microbubble cell sorter for microfluidic flow cytometry.Cytometry A. 2018 Feb;93(2):222-231. doi: 10.1002/cyto.a.23296. Epub 2018 Jan 18. Cytometry A. 2018. PMID: 29346713
-
Hydrodynamic gating valve for microfluidic fluorescence-activated cell sorting.Anal Chim Acta. 2010 Mar 17;663(1):1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2010.01.046. Epub 2010 Feb 1. Anal Chim Acta. 2010. PMID: 20172088
-
A high-throughput acoustic cell sorter.Lab Chip. 2015 Oct 7;15(19):3870-3879. doi: 10.1039/c5lc00706b. Lab Chip. 2015. PMID: 26289231 Free PMC article.
-
Reimagining Flow Cytometric Cell Sorting.Adv Biosyst. 2020 Aug;4(8):e2000019. doi: 10.1002/adbi.202000019. Epub 2020 Jun 2. Adv Biosyst. 2020. PMID: 32483933 Review.
-
Sex-sorting sperm using flow cytometry/cell sorting.Methods Mol Biol. 2013;927:279-95. doi: 10.1007/978-1-62703-038-0_26. Methods Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 22992923 Review.
Cited by
-
Enhancing cell characterization with microfluidics and AI: a comprehensive review of mechanical, electrical, and hybrid techniques.Biotechnol Rep (Amst). 2025 Jul 22;47:e00905. doi: 10.1016/j.btre.2025.e00905. eCollection 2025 Sep. Biotechnol Rep (Amst). 2025. PMID: 40735651 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Editorial Perspective: Advancements in Microfluidics and Biochip Technologies.Micromachines (Basel). 2025 Jan 11;16(1):77. doi: 10.3390/mi16010077. Micromachines (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39858732 Free PMC article.
-
Spatial microfluidic holographic integrated platform for label-free and high-dimensional analysis of cancer heterogeneity.Nat Commun. 2025 Jul 1;16(1):5890. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-60897-w. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40595519 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Role of Artificial Intelligence in Smart Healthcare: A Capability and Function-Oriented Review.Healthcare (Basel). 2025 Jul 8;13(14):1642. doi: 10.3390/healthcare13141642. Healthcare (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40724669 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Machine Learning-Powered Smart Healthcare Systems in the Era of Big Data: Applications, Diagnostic Insights, Challenges, and Ethical Implications.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 Jul 30;15(15):1914. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15151914. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40804880 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Boutros, M., Heigwer, F. & Laufer, C. Microscopy-based high-content screening. Cell163, 1314–1325 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Lai, QueenieT. K. et al. High-throughput time-stretch imaging flow cytometry for multi-class classification of phytoplankton. Opt. Express24, 28170–28184 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Mikami, H. et al. Ultrafast confocal fluorescence microscopy beyond the fluorescence lifetime limit. Optica5, 117–126 (2018).
-
- Lei, C. et al. High-throughput imaging flow cytometry by optofluidic time-stretch microscopy. Nat. Protoc.13, 1603–1631 (2018). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

