DNA replication initiation drives focal mutagenesis and rearrangements in human cancers
- PMID: 39738026
- PMCID: PMC11685606
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-55148-3
DNA replication initiation drives focal mutagenesis and rearrangements in human cancers
Abstract
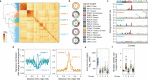
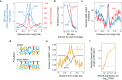
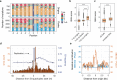
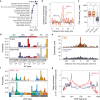
The rate and pattern of mutagenesis in cancer genomes is significantly influenced by DNA accessibility and active biological processes. Here we show that efficient sites of replication initiation drive and modulate specific mutational processes in cancer. Sites of replication initiation impede nucleotide excision repair in melanoma and are off-targets for activation-induced deaminase (AICDA) activity in lymphomas. Using ductal pancreatic adenocarcinoma as a cancer model, we demonstrate that the initiation of DNA synthesis is error-prone at G-quadruplex-forming sequences in tumours displaying markers of replication stress, resulting in a previously recognised but uncharacterised mutational signature. Finally, we demonstrate that replication origins serve as hotspots for genomic rearrangements, including structural and copy number variations. These findings reveal replication origins as functional determinants of tumour biology and demonstrate that replication initiation both passively and actively drives focal mutagenesis in cancer genomes.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Hanahan, D. & Weinberg, R. A. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell144, 646–674 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Dominguez-Sola, D. et al. Non-transcriptional control of DNA replication by c-Myc. Nature448, 445–451 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Di Micco, R. et al. Oncogene-induced senescence is a DNA damage response triggered by DNA hyper-replication. Nature444, 638–642 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Hills, S. A. & Diffley, J. F. X. DNA replication and oncogene-induced replicative stress. Curr. Biol.24, R435–R444 (2014). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

