Aging-induced immune microenvironment remodeling fosters melanoma in male mice via γδ17-Neutrophil-CD8 axis
- PMID: 39738047
- PMCID: PMC11685811
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-55164-3
Aging-induced immune microenvironment remodeling fosters melanoma in male mice via γδ17-Neutrophil-CD8 axis
Abstract
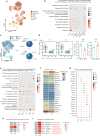
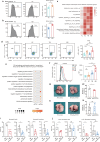
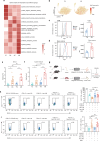
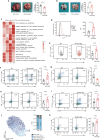
Aging is associated with increased tumor metastasis and poor prognosis. However, how an aging immune system contributes to the process is unclear. Here, single-cell RNA sequencing reveals that in male mice, aging shifts the lung immune microenvironment towards a premetastatic niche, characterized by an increased proportion of IL-17-expressing γδT (γδ17) and neutrophils. Mechanistically, age-dependent downregulation of the immune trafficking receptor S1pr1 drives the expansion of γδ17. Compared to young mice, expanded γδ17 recruit tumor-promoting neutrophils with lower expression levels of CD62L and higher levels of C-kit and CXCR4. These neutrophils suppress the stemness and tumor-killing functions of CD8+ T cells in aged male mice. Accordingly, antibody-mediated depletion of γδT or neutrophils reduces tumor metastatic foci in aged animals, and the administration of the senolytic agent procyanidin C1 reverses the observed immune-mediated, tumor-promoting effects of aging. Thus, we uncover a γδ17-Neutrophil-CD8 axis that promotes aging-driven tumor metastasis in male mice and provides potential insights for managing metastatic tumors.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

