SEAD reference panel with 22,134 haplotypes boosts rare variant imputation and genome-wide association analysis in Asian populations
- PMID: 39738056
- PMCID: PMC11686012
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-55147-4
SEAD reference panel with 22,134 haplotypes boosts rare variant imputation and genome-wide association analysis in Asian populations
Abstract
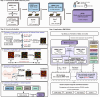
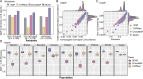
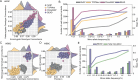
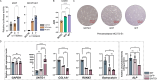
Limited whole genome sequencing (WGS) studies in Asian populations result in a lack of representative reference panels, thus hindering the discovery of ancestry-specific variants. Here, we present the South and East Asian reference Database (SEAD) panel ( https://imputationserver.westlake.edu.cn/ ), which integrates WGS data for 11,067 individuals from various sources across 17 Asian countries. The SEAD panel, comprising 22,134 haplotypes and 88,294,957 variants, demonstrates improved imputation accuracy for South Asian populations compared to 1000 Genomes Project, TOPMed, and ChinaMAP panels, with a higher proportion of well-imputed rare variants. For East Asian populations, SEAD shows concordance comparable to ChinaMAP, but outperforming TOPMed. Additionally, we apply the SEAD panel to conduct a genome-wide association study for total hip (Hip) and femoral neck (FN) bone mineral density (BMD) traits in 5369 genotyped Chinese samples. The single-variant test suggests that rare variants near SNTG1 are associated with Hip BMD (rs60103302, MAF = 0.0092, P = 1.67 × 10-7), and variant-set analysis further supports the association (Pslide_window = 9.08 × 10-9, Pgene_centric = 5.27 × 10-8). This association was not reported previously and can only be detected by using Asian reference panels. Preliminary in vitro experiments for one of the rare variants identified provide evidence that it upregulates SNTG1 expression, which could in turn inhibit the proliferation and differentiation of preosteoblasts.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: S.-H.Y., W.-W.Z. and J.-Q.L. Y.S. are employee of KingMed Diagnostics Co., Ltd. The other authors have no competing interests to declare.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

