Wearable non-invasive neuroprosthesis for targeted sensory restoration in neuropathy
- PMID: 39738088
- PMCID: PMC11686223
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-55152-7
Wearable non-invasive neuroprosthesis for targeted sensory restoration in neuropathy
Abstract
Peripheral neuropathy (PN), the most common complication of diabetes, leads to sensory loss and associated health issues as pain and increased fall risk. However, present treatments do not counteract sensory loss, but only partially manage its consequences. Electrical neural stimulation holds promise to restore sensations, but its efficacy and benefits in PN damaged nerves are yet unknown. We designed a wearable sensory neuroprosthesis (NeuroStep) providing targeted neurostimulation of the undamaged nerve portion and assessed its functionality in 14 PN participants. Our system partially restored lost sensations in all participants through a purposely calibrated neurostimulation, despite PN nerves being less sensitive than healthy nerves (N = 22). Participants improved cadence and functional gait and reported a decrease of neuropathic pain after one day. Restored sensations activated cortical patterns resembling naturally located foot sensations. NeuroStep restores real-time intuitive sensations in PN participants, holding potential to enhance functional and health outcomes while advancing effective non-invasive neuromodulation.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors do not have anything to disclose.
Figures




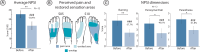


References
-
- WHO. Global report on diabetes. https://www.who.int/publications-detail-redirect/9789241565257 (2016).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- Moveit 197271/Schweizerischer Nationalfonds zur Förderung der Wissenschaftlichen Forschung (Swiss National Science Foundation)
- 320030_175616/Schweizerischer Nationalfonds zur Förderung der Wissenschaftlichen Forschung (Swiss National Science Foundation)
- 759998/EC | EU Framework Programme for Research and Innovation H2020 | H2020 Priority Excellent Science | H2020 European Research Council (H2020 Excellent Science - European Research Council)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

