Unsupervised inter-domain transformation for virtually stained high-resolution mid-infrared photoacoustic microscopy using explainable deep learning
- PMID: 39738110
- PMCID: PMC11685655
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-55262-2
Unsupervised inter-domain transformation for virtually stained high-resolution mid-infrared photoacoustic microscopy using explainable deep learning
Abstract
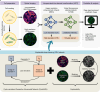
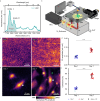
Mid-infrared photoacoustic microscopy can capture biochemical information without staining. However, the long mid-infrared optical wavelengths make the spatial resolution of photoacoustic microscopy significantly poorer than that of conventional confocal fluorescence microscopy. Here, we demonstrate an explainable deep learning-based unsupervised inter-domain transformation of low-resolution unlabeled mid-infrared photoacoustic microscopy images into confocal-like virtually fluorescence-stained high-resolution images. The explainable deep learning-based framework is proposed for this transformation, wherein an unsupervised generative adversarial network is primarily employed and then a saliency constraint is added for better explainability. We validate the performance of explainable deep learning-based mid-infrared photoacoustic microscopy by identifying cell nuclei and filamentous actins in cultured human cardiac fibroblasts and matching them with the corresponding CFM images. The XDL ensures similar saliency between the two domains, making the transformation process more stable and more reliable than existing networks. Our XDL-MIR-PAM enables label-free high-resolution duplexed cellular imaging, which can significantly benefit many research avenues in cell biology.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: J.A. and C.K. have financial interests in OPTICHO, which, however, did not support this work. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Pawley, J. Handbook of Biological Confocal Microscopy, 236. (Springer Science & Business Media, 2006).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

