A Greedy Tabu Dual Heuristic algorithm for the cyclic pickup and delivery problem with 3D loading constraints
- PMID: 39738237
- PMCID: PMC11685623
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-82534-0
A Greedy Tabu Dual Heuristic algorithm for the cyclic pickup and delivery problem with 3D loading constraints
Abstract
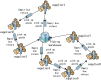
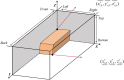
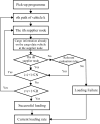
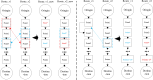
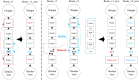
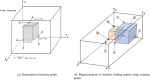
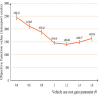
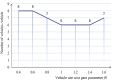
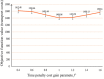
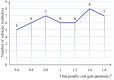
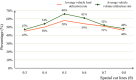
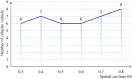
The optimization of auto parts supply chain logistics plays a decisive role in the development of the automotive industry. To reduce logistics costs and improve transportation efficiency, this paper addresses the joint optimization problem of multi-vehicle pickup and delivery transportation paths under time window constraints, coupled with the three-dimensional loading of goods. The model considers mixed time windows, three-dimensional loading constraints, cyclic pickup and delivery paths, varying vehicle loads and volumes, flow balance, and time window constraints. Evaluation rules for the three-dimensional loading test of goods are also set, resulting in constructing a comprehensive optimization model for the inbound logistics of auto parts and components. In this study, a Greedy-Tabu Dual-Heuristic algorithm is proposed, which integrates an Improved Greedy Algorithm with an Enhanced Tabu Search Algorithm based on the ɛ-sampling strategy. The overall problem-solving process for the Improved Greedy Algorithm and the Tabu Search Algorithm is outlined. The superiority, efficiency, and stability of the improved algorithm are verified by solving cases of various sizes and analyzing the algorithm's results before and after improvement. A case study involving the third-party logistics company R Enterprise compares the pickup and delivery-separated Milk-Run mode with the simultaneous delivery and pickup Milk-Run mode. The proposed method shows a 26.67% reduction in total distance traveled and a 46.60% decrease in waiting time compared to the traditional Milk-Run approach. Additionally, when evaluated against the standard 3D loading inspection method, the proposed approach improves average vehicle load utilization by 17% and vehicle volume utilization by 15%. These findings verify the applicability and superiority of the proposed algorithms and models in practical scenarios.
Keywords: Cyclic pickup and delivery; Hybrid multi-model; Path optimization; Three-dimensional loading.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures







References
-
- Zhou, B. & Wen, M. A mutli-objective artificial electric field algorithm with reinforcement learning for milk-run assembly line feeding and scheduling problem. Comput. Ind. Eng.190, 110080. 10.1016/J.CIE.2024.110080 (2024).
-
- Mei, H., Jingshuai, Y., Teng, M., Xiuli, L. & Ting, W. The modeling of milk-run vehicle routing problem based on improved c-w algorithm that joined time window. Transportation Research Procedia25, 716–728. 10.1016/j.trpro.2017.05.453 (2017). World Conference on Transport Research - WCTR 2016 Shanghai. 10-15 July 2016.
-
- Molina, J. C., Salmeron, J. L. & Eguia, I. An ACS-based memetic algorithm for the heterogeneous vehicle routing problem with time windows. Expert Syst. Appl.157, 113379. 10.1016/J.ESWA.2020.113379 (2020).
-
- Moura, A., Pinto, T., Alves, C. & Valério de Carvalho, J. A matheuristic approach to the integration of three-dimensional bin packing problem and vehicle routing problem with simultaneous delivery and pickup. Mathematics[SPACE]10.3390/math11030713 (2023).
-
- Marques, A., Soares, R., Santos, M. J. & Amorim, P. Integrated planning of inbound and outbound logistics with a rich vehicle routing problem with backhauls. Omega92, 102172. 10.1016/j.omega.2019.102172 (2020).
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

