The effect of stroboscopic vision training on the performance of elite curling athletes
- PMID: 39738499
- PMCID: PMC11685645
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-82685-0
The effect of stroboscopic vision training on the performance of elite curling athletes
Abstract
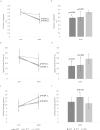
The aim of the study was to investigate the impacts of four weeks of stroboscopic vision training (SVT) and four weeks of temporal feedback training (TFT) on elite curling athletes' duration judgment, as well as stone delivery performance (delivery speed control and accuracy). Thirty national-level curling athletes were selected as participants and randomly assigned to either the SVT group (wearing stroboscopic glasses: the strobe frequencies increased weekly from Level 1 to Level 4.), the TFT group (using a timing system to provide feedback on stone delivery time), or a control group. Apart from the differences in training methods, the intervention programme was identical across the three groups, with each group performing stone delivery training three times per week for 40 min per session. The training regimen consisted of a 'ladder' drill targeting the house (effective zones 4-10), with the sequence of training increasing and then decreasing in complexity. Repeated measures ANOVA (3 × 2) and post-hoc tests (Bonferroni) were used to analyse the effects of different training methods. The results showed that the four-week training intervention produced significant interactions in duration judgment (p = 0.005, f = 0.692) and accuracy (p = 0.001, f = 0.805). SVT significantly improved duration judgment (p < 0.001, d = 2.374) and delivery speed control (p = 0.011, d = 1.421). TFT significantly improved delivery accuracy (p = 0.015, d = 1.364). Four weeks of SVT and TFT both improved duration judgment, curling speed control performance among elite curling athletes. In terms of accuracy improvement, four weeks of TFT yielded greater benefits than SVT.
Keywords: Curling performance; Elite curling athletes; Stroboscopic vision training.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Institutional review board statement: The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Sports Science Experiment Ethics Committee of Beijing Sport University (2023270H). Informed consent statement: Informed consent was obtained from all participants involved in the study. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Erhan, S. E., Ağduman, F. & Bedir, D. Exploring predictors of team performance in curling championships: an investigation of factors predicting success. CBÜ Beden Eğitimi ve Spor Bilimleri Dergisi18, 845–853 (2023).
-
- Otani, H., Masui, F., Hirata, K., Yanagi, H. & Ptaszynski, M. In icSPORTS. 182–187.
-
- YY, F. Study on the correlation between the balance ability, core strength and throwing performance of curling players Master thesis, (Jilin Sport University, 2020).
-
- Schmidt, R. A., Lee, T. D., Winstein, C., Wulf, G. & Zelaznik, H. N. Motor Control and Learning: A Behavioral Emphasis. (Human Kinetics, 2018).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 2021QN015/Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities and the Chinese Universities Scientific Fund
- 2021QN015/Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities and the Chinese Universities Scientific Fund
- 2021QN015/Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities and the Chinese Universities Scientific Fund
- 2021QN015/Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities and the Chinese Universities Scientific Fund
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

