The relationship between complete blood cell count-derived inflammatory biomarkers and erectile dysfunction in the United States
- PMID: 39738513
- PMCID: PMC11685723
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-83733-5
The relationship between complete blood cell count-derived inflammatory biomarkers and erectile dysfunction in the United States
Abstract
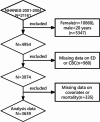
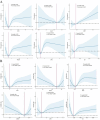
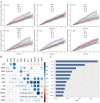
Erectile dysfunction(ED), a prevalent condition within the male genitourinary system, significantly impairs the quality of life for affected men. Although certain inflammatory indicators, such as the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio(NLR), systemic inflammatory response index (SIRI), and systemic immune-inflammation index(SII), have been linked to ED, the correlation with other markers and their impact on survival outcomes in ED patients remain largely unexplored. This research aims to investigate the correlation between inflammatory biomarkers derived from a complete blood cell count(CBC) and the occurrence of ED. Data regarding ED were extracted from the 2001-2004 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey(NHANES), and mortality events were ascertained through the National Death Index up to December 2019. The CBC-derived inflammatory indicators assessed in this study included the NLR, derived neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio(dNLR), monocyte-to-lymphocyte ratio(MLR), neutrophil-monocyte to lymphocyte ratio (NMLR), SIRI, and SII. The prognostic significance of these CBC-derived inflammatory indicators was evaluated using random survival forests(RSF) analysis. Our study encompassed a cohort of 3,639 individuals, among whom 1,031 were diagnosed with ED. Among individuals with ED, 610 experienced all-cause mortality. Following adjustment for all confounding variables, it was observed that elevated levels of NLR(OR = 1.09, 95%CI 1.00-1.19, p = 0.021), MLR (OR = 2.97, 95% CI 1.18-7.50, p = 0.01), NMLR(OR = 1.10, 95% CI 1.01-1.11, p = 0.006), and SIRI(OR = 1.11, 95% CI 1.01-1.22, p = 0.017) were associated with an increased prevalence of ED. Among participants with ED, those in the highest quartile of NLR(HR = 1.06, 95% CI 1.00-1.11, p = 0.032), MLR(HR = 2.00, 95% CI 1.33-3.01, p < 0.001), NMLR (HR = 1.06, 95% CI 1.01-1.11, p = 0.024), and SII(HR = 1.00, 95% CI 1.00-1.00, p = 0.015) exhibited an elevated risk of all-cause mortality compared to those in the lower levels of inflammation-derived indicators. Our research suggests that, compared with other inflammatory markers derived from complete blood cell count, MLR has the highest predictive power for the prevalence of ED and all-cause mortality in these populations.
Keywords: Complete blood cell; Cross-sectional study; Erectile dysfunction; Inflammatory markers; NHANES.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Conflict of interest: The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Associations of CBC-Derived inflammatory indicators with sarcopenia and mortality in adults: evidence from Nhanes 1999 ∼ 2006.BMC Geriatr. 2024 May 16;24(1):432. doi: 10.1186/s12877-024-05012-2. BMC Geriatr. 2024. PMID: 38755603 Free PMC article.
-
Association between inflammation indicators (MLR, NLR, SII, SIRI, and AISI) and erectile dysfunction in US adults: NHANES 2001-2004.J Health Popul Nutr. 2024 Oct 26;43(1):169. doi: 10.1186/s41043-024-00667-4. J Health Popul Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39462407 Free PMC article.
-
Association between complete blood count-derived inflammatory markers and the risk of frailty and mortality in middle-aged and older adults.Front Public Health. 2024 Jul 31;12:1427546. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1427546. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39145178 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of inflammatory markers NLR, PLR, LMR, dNLR, ANC in melanoma patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: a meta-analysis and systematic review.Front Immunol. 2024 Oct 18;15:1482746. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1482746. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39493767 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of hematologic inflammatory markers on the prognosis of geriatric hip fracture: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur J Med Res. 2024 Dec 19;29(1):609. doi: 10.1186/s40001-024-02211-w. Eur J Med Res. 2024. PMID: 39702270 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Neutrophil-and-monocyte-to-lymphocyte ratio is positively associated with elevated prostate-specific antigen levels and high-risk prostate cancer: evidence from the NHANES (2003-2008).Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025 Apr 25;13:1573932. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1573932. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 40352665 Free PMC article.
References
-
- NIH Consensus Conference. Impotence. NIH Consensus Development Panel on Impotence. Jama. ;270(1):83–90. (1993). - PubMed
-
- Mark, K. P. et al. Erectile dysfunction prevalence in the United States: report from the 2021 National Survey of sexual wellbeing. J. Sex. Med.21 (4), 296–303 (2024). - PubMed
-
- Randrup, E., Baum, N. & Feibus, A. Erectile dysfunction and cardiovascular disease. Postgrad. Med.127 (2), 166–172 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Westheide, J. et al. Sexuality in male psychiatric inpatients. A descriptive comparison of psychiatric patients, patients with epilepsy and healthy volunteers. Pharmacopsychiatry40 (5), 183–190 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Zhao, B. et al. Erectile Dysfunction predicts Cardiovascular events as an independent risk factor: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. J. Sex. Med.16 (7), 1005–1017 (2019). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

