Accelerated treatment concept in postpneumonectomy empyema with bronchopleural fistula
- PMID: 39738609
- PMCID: PMC11686295
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-83334-2
Accelerated treatment concept in postpneumonectomy empyema with bronchopleural fistula
Abstract
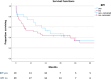
Treatment of postpneumonectomy empyema remains challenging, especially in presence of bronchopleural fistula. We analysed clinical outcome data of patients with and without bronchopleural fistula undergoing an accelerated empyema treatment concept. From November 2005 to July 2020, all patients with postpneumonectomy empyema were included. Therapy consisted of repeated surgical debridement of the pleural cavity, evaluation for loco-regional flap, negative pressure wound therapy and definitive closure after installation an antibiotic solution in the cavity. Primary endpoint was perioperative mortality, focusing on comparison between patients with (= group A) and without bronchopleural fistula (= group B). Secondary endpoints were empyema resolution/recurrence and length of stay. 58 patients underwent the treatment concept: 19 (32.8%) with bronchopleural fistula. Patients' mean age was 62.7 ± 11.5 years. Nine patients (15.5%) deceased within 30 days: 3 (15.8%) in group A, 6 (15.4%) in group B. 90-days mortality tends to be lower in group A (n = 3 (15.8%)) compared to group B (n = 11 (28.2%)) (p = 0.078). Incidence of postoperative complication was 63.2% (n = 12) in group A compared to 56.4% (n = 22) in group B (p = 0.316). Postpneumonectomy empyema resolution was 100% in the cohort. 3 patients (15.8%) in the group A and 3 (7.7%) in group B (p = 0.175) developed an empyema-recurrence, successfully managed with the treatment concept again. Mean hospital length of stay was lower in group A (24.6 ± 9.5 days vs 27.2 ± 24.3 days in group B; p = 0.329). With our accelerated treatment concept, postpneumonectomy empyema with bronchopleural fistula could effectively and safely be treated while maintaining integrity of the chest wall. Clinical Registration Number: KEK-ZH-NR: 2021-01114.
Keywords: Accelerated treatment concept (Zurich concept); Bronchopleural fistula; Postpneumonectomy empyema.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: Isabelle Opitz: Roche (Institutional Grant and Speakers Bureau), AstraZeneca (Advisory Board and Speakers Bureau), MSD (Advisory Board), BMS (Advisory Board), Medtronic (Institutional Grant), Intuitive (Proctorship). The other authors have no competing interests.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

