RBM4-mediated intron excision of Hsf1 induces BDNF for cerebellar foliation
- PMID: 39738787
- PMCID: PMC11685446
- DOI: 10.1038/s42003-024-07328-6
RBM4-mediated intron excision of Hsf1 induces BDNF for cerebellar foliation
Abstract
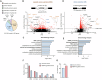
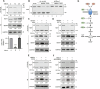
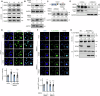
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) plays important roles in brain development and neural function. Constitutive knockout of the splicing regulator RBM4 reduces BDNF expression in the developing brain and causes cerebellar hypoplasia, an autism-like feature. Here, we show that Rbm4 knockout induced intron 6 retention of Hsf1, leading to downregulation of HSF1 protein and its downstream target BDNF. RBM4-mediated Hsf1 intron excision regulated BDNF expression in cultured granule cells. Ectopic expression of HSF1 restored cerebellar foliation and motor learning of Rbm4-knockout mice, indicating a critical role for RBM4-HSF1-BDNF in cerebellar foliation. Moreover, N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) signaling promoted the expression and nuclear translocation of RBM4, and hence increased the expression of both HSF and BDNF. A short CU-rich motif was responsible for NMDAR- and RBM4-mediated intron excision. Finally, RBM4 and polypyrimidine tract binding (PTB) proteins play antagonistic roles in intron excision, suggesting a role for splicing regulation in BDNF expression.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

