Chirality-Induced Hydroxyapatite Manipulates Enantioselective Bone-Implant Interactions Toward Ameliorative Osteoporotic Osseointegration
- PMID: 39738981
- PMCID: PMC11848601
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202411602
Chirality-Induced Hydroxyapatite Manipulates Enantioselective Bone-Implant Interactions Toward Ameliorative Osteoporotic Osseointegration
Abstract
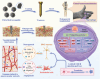
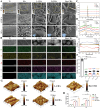
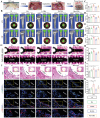
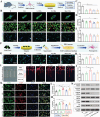
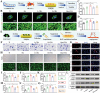
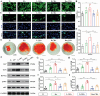
Inspired by the fundamental attribute of chirality in nature, chiral-engineered biomaterials now represent a groundbreaking frontier in biomedical fields. However, the integration of chirality within inorganic materials remains a critical challenge and developments of chirality-induced bionic bone implants are still in infancy. In this view, novel chiral hydroxyapatite (CHA) coated Ti alloys are successfully synthesized by a sophisticated chiral molecule-induced self-assembly method for the first time. The obtained samples are characterized by stereospecific L-/D-/Rac-chiral hierarchical morphology, nanotopography rough surfaces, improved hydrophilicity, and bioactivity. Following implantation into rat femoral condyle defects, the distinct stereospecific chiral hierarchical structures exhibit highly enantioselective bone-implants interactions, wherein the left-handed chirality of L-CHA strongly promotes osteoporotic osseointegration and vice versa for right-handed chirality of D-CHA. Consistently, in vitro assays further validate the superior enantiomer-dependent osteoporotic osseointegration ability of L-CHA, mainly by manipulating desired immunomodulation coupled with enhanced neurogenesis, angiogenesis, and osteogenesis. Moreover, as analyzed by transcriptomic RNA-seq, a new discovery of down-regulated IL-17 signaling pathway is considered predominately responsible for the desired immunomodulation ability of L-CHA. These results provide new insights into biological multifunctionality and mechanism underlying L-chirality's roles for bone healing, thus may inspiring developments of new generation of chiral biomaterials.
Keywords: chirality; enantioselectivity; hydroxyapatite; immunomodulation; osteoporotic osseointegration.
© 2024 The Author(s). Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Zhao Y. N., Kang H. L., Wu X. P., Zhuang P. Z., Tu R., Goto T., Li F., Dai H. L., Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2023, 12, e2203099. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
