A novel histone acetylation-associated gene signature with prognostic value in Ewing sarcoma
- PMID: 39738986
- PMCID: PMC11685356
- DOI: 10.1007/s12672-024-01689-4
A novel histone acetylation-associated gene signature with prognostic value in Ewing sarcoma
Abstract
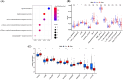
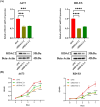
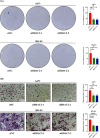
Histone acetylation is an important epigenetic modification, modulating the development of many tumors. However, the functions of most histone acetylation-related genes (HARGs) and their prognostic values in Ewing sarcoma (EWS) remain unclear. The current study aimed to investigate the prognostic values and potential functions of HARGs in EWS. After collecting EWS patients with mRNA sequencing data from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database and a list of HARGs from previous studies, Cox regression and Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator (LASSO) regression were performed to construct a prognostic gene signature based on HARGs. Then, four HARGs (TAF4, ATF2, HDAC2 and OGA) composed a formula to calculate risk score for each patient in the training cohort. Based on median risk score, all patients were classified into low- and high-risk group, and patients with high-risk score had a poor survival outcome (p < 0.001). The 1-, 2-,3- and 5-year AUC (0.853, 0.886,0.909and 0.833, respectively) showed the good ability of this signature to predict the prognoses of EWS patients. In addition, distinct functional enrichment and immune-related pathways were also observed in two risk groups. All results were validated in an external cohort from two dataset in GEO database. Moreover, it was found that silencing HDAC2 expression in EWS cells significantly suppressed the cell viability and migration capability. In conclusion, this is the first study to detect the prognostic values of HARGs in EWS patients, further developing a good prognostic signature based on HARGs, and HDAC2 might be an oncogene in the development of EWS.
Keywords: Ewing sarcoma; HDAC2; Histone acetylation; Prognostic signature.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A Novel Defined Hypoxia-Related Gene Signature for Prognostic Prediction of Patients With Ewing Sarcoma.Front Genet. 2022 Jun 2;13:908113. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.908113. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35719404 Free PMC article.
-
A seven-lncRNA signature for predicting Ewing's sarcoma.PeerJ. 2021 Jun 17;9:e11599. doi: 10.7717/peerj.11599. eCollection 2021. PeerJ. 2021. PMID: 34178467 Free PMC article.
-
Histone acetylation modification regulator-mediated tumor microenvironment infiltration characteristics and prognostic model of lung adenocarcinoma patients.J Thorac Dis. 2022 Oct;14(10):3886-3902. doi: 10.21037/jtd-22-1000. J Thorac Dis. 2022. PMID: 36389327 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of lactate-related signatures correlates with immunosuppressive microenvironment and prognostic prediction in ewing sarcoma.Front Genet. 2022 Aug 24;13:965126. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.965126. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36092937 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of myeloid signature genes for predicting prognosis and immune landscape in Ewing sarcoma.Cancer Sci. 2023 Apr;114(4):1240-1255. doi: 10.1111/cas.15688. Epub 2022 Dec 19. Cancer Sci. 2023. PMID: 36478349 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Unraveling the role of histone acetylation in sepsis biomarker discovery.Front Mol Biosci. 2025 Apr 30;12:1582181. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2025.1582181. eCollection 2025. Front Mol Biosci. 2025. PMID: 40370519 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
