Portulaca oleracea Extract Ameliorates Testosterone Propionate-Induced Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia in Male Sprague-Dawley Rats
- PMID: 39739367
- PMCID: PMC11687364
- DOI: 10.1002/vms3.70184
Portulaca oleracea Extract Ameliorates Testosterone Propionate-Induced Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia in Male Sprague-Dawley Rats
Abstract
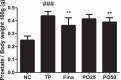
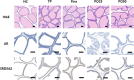
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is a distressing health problem that can cause serious complications in aging men. Androgens are implicated in the causation of BPH. Portulaca oleracea (PO) is a natural product with diverse pharmacological effects. The objective of this study was to investigate the effect of PO in a rat model of testosterone propionate (TP)-induced BPH and explore the underlying mechanisms. Thirty-five Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats were divided into the following equal groups (n = 7): normal control (NC) group, TP (3 mg/kg) group, finasteride (10 mg/kg) group, 25 and 50 mg/kg PO groups. At the end of the experiment, the body weights (BWs) of the rats were measured before they were euthanized to the establishment obtain serum and prostate weight (PW). TP-induced levels of androgen-related proteins in the prostate were also investigated. In the TP group, prostate size, BW, serum DHT level, prostate epithelial cell thickness and androgen-related protein level were higher than those in the NC group (p < 0.001). PO reversed TP-induced BPH in a dose-dependent manner (p < 0.01) and its effect was similar to that of finasteride. A similar effect of PO on the androgen-related protein level was also observed. We successfully established a TP-induced BPH rat model. This is the first study to demonstrate that inhibition of androgen-related proteins using PO can alleviate BPH.
Keywords: Portulaca oleracea; androgen‐related proteins; benign prostatic hyperplasia; testosterone propionate.
© 2024 The Author(s). Veterinary Medicine and Science published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
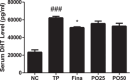
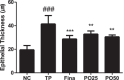

References
-
- Abdullah, M. S. , and Kusumaningtyas R. D.. 2020. “The Extraction of Purslane (Portulaca oleracea L.) Using Alcohol Solvents 48% and Its Utilization as a Source of Encapsulated Omega‐3 Oil.” In AIP Conference Proceedings. Melville, NY: AIP Publishing.
-
- Alawamlh, O. A. H. , Goueli R., and Lee R. K.. 2018. “Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms, Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia, and Urinary Retention.” Medical Clinics of North America 102: 301–311. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

