Two Hits of EDCs Three Generations Apart: Evaluating Multigenerational Anxiety-Like Behavioral Phenotypes in Male Rats Exposed to Aroclor 1221 and Vinclozolin
- PMID: 39739410
- PMCID: PMC11687611
- DOI: 10.1289/EHP15684
Two Hits of EDCs Three Generations Apart: Evaluating Multigenerational Anxiety-Like Behavioral Phenotypes in Male Rats Exposed to Aroclor 1221 and Vinclozolin
Abstract
Background: Increasing evidence supports an association of endocrine-disrupting chemical (EDC) exposures with adverse biological effects in humans and wildlife. Recent studies reveal that health consequences of environmental exposures may persist or emerge across generations. This creates a dual conundrum: that we are exposed to contemporary environmental chemicals overlaid upon the inheritance of our ancestors' exposure profiles. Even when legacy EDCs are phased out, they may remain relevant due to persistence in the environment together with intergenerational inheritance of their adverse biological effects. Thus, we all possess a body burden of legacy contaminants, and we are also increasingly exposed to new generations of EDCs.
Objectives: We assessed the effects of direct and ancestral exposures to EDCs across six generations on anxiety-like behaviors in male rats using our "two hits, three generations apart" multigenerational EDC exposure experimental model. We investigated two classes of EDCs with distinct hormonal actions and historical use-the weakly estrogenic polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB) mixture Aroclor 1221 (A1221) and the anti-androgenic fungicide vinclozolin (VIN)-in both the maternal and paternal line. We also determined if a hormonal mechanism drives these effects across generations.
Methods: Rats were gestationally exposed to A1221, VIN, or vehicle [dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO)] in the F1 generation. Three generations later, the F4 generation was given the same or a different exposure. Anxiety-like behavior was measured in the open field test, light:dark box, and elevated plus maze across generations. Serum was collected at the end of the experiment, and concentrations of estradiol and corticosterone were analyzed.
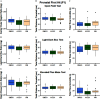
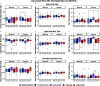
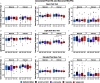
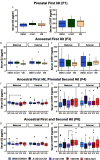
Results: Although direct exposure did not affect behavior in F1 males, ancestral exposure to VIN decreased anxiety-like behavior in the F3 paternal line compared to vehicle. In the F4 paternal line, ancestral A1221 followed by direct exposure to VIN increased anxiety-like behavior compared to controls. In the F6 maternal line, relative to vehicle, the double ancestral hits of A1221/VIN decreased anxiety-like behavior. Serum hormones weakly predicted behavioral changes in the F4 paternal line and were modestly affected in the F4 and F6 maternal lines.
Discussion: Our data suggest that anxiety-like behavioral phenotypes emerge transgenerationally in male rats in response to EDC exposure and that multiple hits of either the same or a different EDC can increase the impact in a lineage-specific manner. https://doi.org/10.1289/EHP15684.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Two Hits of EDCs Three Generations Apart: Evaluating Multigenerational Anxiety-Like Behavioral Phenotypes in Female Rats Exposed to Aroclor 1221 and Vinclozolin.Environ Health Perspect. 2024 Dec;132(12):127005. doi: 10.1289/EHP15621. Epub 2024 Dec 31. Environ Health Perspect. 2024. PMID: 39739409 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of the Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals, Vinclozolin and Polychlorinated Biphenyls, on Physiological and Sociosexual Phenotypes in F2 Generation Sprague-Dawley Rats.Environ Health Perspect. 2018 Sep;126(9):97005. doi: 10.1289/EHP3550. Environ Health Perspect. 2018. PMID: 30212226 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal care modulates transgenerational effects of endocrine-disrupting chemicals on offspring pup vocalizations and adult behaviors.Horm Behav. 2019 Jan;107:96-109. doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2018.12.009. Epub 2019 Jan 4. Horm Behav. 2019. PMID: 30576639 Free PMC article.
-
A proposed framework for the systematic review and integrated assessment (SYRINA) of endocrine disrupting chemicals.Environ Health. 2016 Jul 14;15(1):74. doi: 10.1186/s12940-016-0156-6. Environ Health. 2016. PMID: 27412149 Free PMC article.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Darbre PD. 2019. The history of endocrine-disrupting chemicals. Curr Opin Endocr Metab Res 7:26–33, 10.1016/j.coemr.2019.06.007. - DOI
-
- Hilz EN, Gore AC. 2023. Endocrine-disrupting chemicals: science and policy. Policy Insights Behav Brain Sci 10(2):142–150, 10.1177/23727322231196794. - DOI
-
- Borja J, Taleon DM, Auresenia J, Gallardo S. 2005. Polychlorinated biphenyls and their biodegradation. Process Biochem 40(6):1999–2013, 10.1016/j.procbio.2004.08.006. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

