Alterations in gut-derived uremic toxins before the onset of azotemic chronic kidney disease in cats
- PMID: 39739435
- PMCID: PMC11683462
- DOI: 10.1111/jvim.17289
Alterations in gut-derived uremic toxins before the onset of azotemic chronic kidney disease in cats
Abstract
Background: Although gut-derived uremic toxins are increased in azotemic chronic kidney disease (CKD) in cats and implicated in disease progression, it remains unclear if augmented formation or retention of these toxins is associated with the development of renal azotemia.
Objectives: Assess the association between gut-derived toxins (ie, indoxyl-sulfate, p-cresyl-sulfate, and trimethylamine-N-oxide [TMAO]) and the onset of azotemic CKD in cats.
Animals: Forty-eight client-owned cats.
Methods: Nested case-control study, comparing serum and urine gut-derived uremic toxin abundance at 6-month intervals between initially healthy cats that developed azotemic CKD (n = 22) and a control group (n = 26) that remained healthy, using a targeted metabolomic approach.
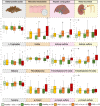
Results: Cats in the CKD group had significantly higher serum indoxyl-sulfate (mean [SD], 1.44 [1.06] vs 0.83 [0.46]; P = .02) and TMAO (mean [SD], 1.82 [1.80] vs 1.60 [0.62]; P = .01) abundance 6 months before the detection of azotemic CKD. Furthermore, logistic regression analysis indicated that indoxyl-sulfate (odds ratio [OR]: 3.2; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.2-9.0; P = .04) and TMAO (OR: 3.9; 95% CI: 1.4-11; P = .03) were predictors for the onset of azotemia 6 months before diagnosis. However, renal function biomarkers creatinine, symmetric dimethylarginine, and urinary specific gravity were significantly correlated with indoxyl-sulfate and TMAO abundance, causing a loss in predictive significance after correction for these factors.
Conclusions: Impaired gut-derived uremic toxin handling is apparent at least 6 months before the diagnosis of azotemia, likely reflecting an already ongoing decrease in GFR, tubular function, or both. A direct causal relationship between gut-derived uremic toxicity and the initiation of CKD in cats is still lacking.
Keywords: CKD development; early intervention; feline chronic kidney disease; pathophysiology; uremic toxicity.
© 2024 The Author(s). Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American College of Veterinary Internal Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Vanholder R, Glorieux G. Uremic toxicity. In: Nissenson AR, Fine RN, eds. Handbook of Dialysis Therapy. 6th ed. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 2023:16‐44. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-323-79135-9.00002-1 - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
