Viral-Mediated Connexin 26 Expression Combined with Dexamethasone Rescues Hearing in a Conditional Gjb2 Null Mice Model
- PMID: 39739601
- PMCID: PMC12362743
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202406510
Viral-Mediated Connexin 26 Expression Combined with Dexamethasone Rescues Hearing in a Conditional Gjb2 Null Mice Model
Abstract
GJB2 encodes connexin 26 (Cx26), the most commonly mutated gene causing hereditary non-syndromic hearing loss. Cx26 is mainly expressed in supporting cells (SCs) and fibrocytes in the mammalian cochlea. Gene therapy is currently considered the most promising strategy for eradicating genetic diseases. However, there have been no significant effects of gene therapy for GJB2 gene mutation-associated deafness because deficiency of Cx26 leads to expanded sensory epithelial damage. In this study, the AAV2.7m8 serotype combined with the gfaABC1D promoter targeted infection of SCs is identified. It is found that Gjb2 gene replacement therapy in wild-type mice results in sensory hair cells (HCs) deficits, excessive inflammatory responses, and hearing loss. This may be one of the key factors contributing to the hardship of GJB2 gene replacement therapy. Dexamethasone (DEX) shows promising results in inhibiting macrophage recruitment, with a protective effect against HC damage. Further, the combination of AAV2.7m8-Gjb2 with DEX shows a synergistic effect and enhances the gene therapy effect in a conditional Cx26 null mice model. These results indicate that the combination of gene therapy and medication will provide a new strategy for the treatment of hereditary deafness associated with GJB2 defects.
Keywords: AAV2.7m8; GJB2; dexamethasone; gene therapy; hearing loss.
© 2024 The Author(s). Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

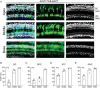
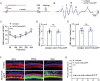

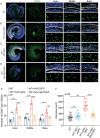


References
-
- Smith R. J., J. F. Bale Jr., White K. R., Lancet 2005, 365, 879. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 82430035/Key Program of the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82301325/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82301323/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82301324/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82071058/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2021YFF0702303/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- 2023YFE0203200/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- 2023AFA038/Foundation for Innovative Research Groups of Hubei Province
- 2024BRA019/Basic Research Support Program of Huazhong University of Science and Technology
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
