Deciphering the interactome of Ataxin-2 and TDP-43 in iPSC-derived neurons for potential ALS targets
- PMID: 39739690
- PMCID: PMC11687654
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0308428
Deciphering the interactome of Ataxin-2 and TDP-43 in iPSC-derived neurons for potential ALS targets
Abstract
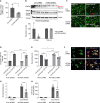
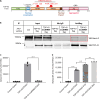
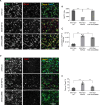
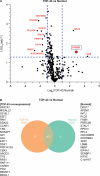
Ataxin-2 is a protein containing a polyQ extension and intermediate length of polyQ extensions increases the risk of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS). Down-regulation of Ataxin-2 has been shown to mitigate TDP-43 proteinopathy in ALS models. To identify alternative therapeutic targets that can mitigate TDP-43 toxicity, we examined the interaction between Ataxin-2 and TDP-43. Co-immunoprecipitation demonstrated that Ataxin-2 and TDP-43 interact, that their interaction is mediated through the RNA recognition motif (RRM) of TDP-43, and knocking down Ataxin-2 or mutating the RRM domains rescued TDP-43 toxicity in an iPSC-derived neuronal model with TDP-43 overexpression. To decipher the Ataxin-2 and TDP-43 interactome, we used co-immunoprecipitation followed by mass spectrometry to identify proteins that interacted with Ataxin-2 and TDP-43 under conditions of endogenous or overexpressed TDP-43 in iPSC-derived neurons. Multiple interactome proteins were differentially regulated by TDP-43 overexpression and toxicity, including those involved in RNA regulation, cell survival, cytoskeleton reorganization, protein modification, and diseases. Interestingly, the RNA-binding protein (RBP), TAF15 which has been implicated in ALS was identified as a strong binder of Ataxin-2 in the condition of TDP-43 overexpression. Together, this study provides a comprehensive annotation of the Ataxin-2 and TDP-43 interactome and identifies potential therapeutic pathways and targets that could be modulated to alleviate Ataxin-2 and TDP-43 interaction-induced toxicity in ALS.
Copyright: © 2024 Tian et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors were employees of Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA at the time of this study. Employment does not alter authors’ adherence to the journal’s policies on conflicts of interest or sharing data and materials.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

