Combination of triciribine and p38 MAPK inhibitor PD169316 enhances the differentiation effect on myeloid leukemia cells
- PMID: 39739720
- PMCID: PMC11687802
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0312406
Combination of triciribine and p38 MAPK inhibitor PD169316 enhances the differentiation effect on myeloid leukemia cells
Abstract
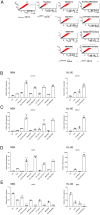
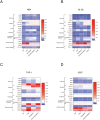
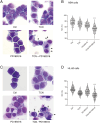
Differentiation therapy with all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) is well established for acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL). However, the narrow application and tolerance development of ATRA remain to be improved. A number of kinase inhibitors have been reported to induce cell differentiation. In this study, we investigated several combinations of these kinase inhibitors. Recently, we revealed that the Akt inhibitor triciribine (TCN) efficiently induces differentiation of NB4 APL cells and acute myeloid leukemia (AML) M2-derived HL-60 cells through activation of the ERK/MAPK pathway. In the present study, we found that the p38 MAPK inhibitor PD169316 had profoundly enhanced the TCN effect for differentiation of NB4 and HL-60 cells. Morphologically, the combination of these two agents efficiently reduced the nuclear-to-cytoplasmic ratio and induced the expression of myelomonocytic markers (CD11b, CD11c) and some ectopic markers (erythroid glycophorin A, lymphoid CD7 and CD20), as determined by PCR and flow cytometry analyses. Western blotting analysis revealed that these agents efficiently induced phosphorylation of ERK. To clarify the molecular mechanisms involved in the TCN and PD169316-induced differentiation, we performed microarray analyses using NB4 cells. Pathway analysis using DAVID software indicated that "viral protein interaction with cytokine and cytokine receptor" and "cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction" were enriched with high significance. Real-time PCR analysis demonstrated that genes for components of these pathways, including chemokines like CCL1, CCL2, CCL3, CCL5, and CXCL8 as well as cytokines and receptors like CSF1, IL-10, IL-10RA, IL-10RB, IL-1β, and TNFSF10, were upregulated in NB4 and HL-60 cells during TCN and PD169316-induced differentiation.
Copyright: © 2024 Sato-Nagaoka et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Identification of triciribine as a novel myeloid cell differentiation inducer.PLoS One. 2024 May 14;19(5):e0303428. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0303428. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38743735 Free PMC article.
-
Fucosylation inhibitor 6-alkynylfucose enhances the ATRA-induced differentiation effect on acute promyelocytic leukemia cells.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2024 May 28;710:149541. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2024.149541. Epub 2024 Jan 29. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2024. PMID: 38608490
-
Inhibition of p38 MAPK Phosphorylation Is Critical for Bestatin to Enhance ATRA-Induced Cell Differentiation in Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia NB4 Cells.Am J Ther. 2016 May-Jun;23(3):e680-9. doi: 10.1097/01.mjt.0000433950.01406.b3. Am J Ther. 2016. PMID: 24141198
-
Reprogramming acute myeloid leukemia into sensitivity for retinoic-acid-driven differentiation.Exp Hematol. 2017 Aug;52:12-23. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2017.04.007. Epub 2017 Apr 27. Exp Hematol. 2017. PMID: 28456748 Review.
-
Kinase Inhibitors and Interferons as Other Myeloid Differentiation Inducers in Leukemia Therapy.Acta Haematol. 2022;145(2):113-121. doi: 10.1159/000519769. Epub 2021 Oct 21. Acta Haematol. 2022. PMID: 34673646 Review.
Cited by
-
As2S2 Mediates the ROS/P38 MAPK Signaling Pathway to Induce Apoptosis and S-Phase Arrest in Myelodysplastic Syndrome Cells.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025 Apr 7;47(4):253. doi: 10.3390/cimb47040253. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40699652 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

