A study of specific immunoglobulin G4 expression in allergic rhinitis and its value in assessing efficacy and in predicting prognosis of sublingual immunotherapy
- PMID: 39739782
- PMCID: PMC11724161
- DOI: 10.1002/kjm2.12916
A study of specific immunoglobulin G4 expression in allergic rhinitis and its value in assessing efficacy and in predicting prognosis of sublingual immunotherapy
Abstract
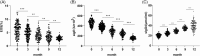
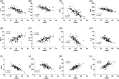
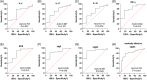
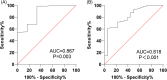
Allergic rhinitis (AR) is a widespread health issue with a rising global prevalence, and sublingual immunotherapy (SLIT) has shown efficacy in AR treatment. We examined specific immunoglobulin G4 (sIgG4) expression in AR and its role in evaluating SLIT efficacy and predicting patient prognosis. We compared total nasal symptom score (TNSS), total medication score (TMS), visual analogue scale (VAS) score, inflammatory cytokines, and immune function markers in AR patients before and after SLIT. SLIT reduced TNSS, TMS, VAS scores, IL-4, IL-17, eosinophilia percentage (EOS%), and specific immunoglobulin E (sIgE) levels, while increasing INF-γ, IL-10, and sIgG4. The sIgG4 level at pre-treatment and 12 months post-treatment was negatively correlated with TNSS, TMS, VAS score, IL-4, IL-17, EOS%, and sIgE, and positively correlated with IFN-γ and IL-10. Most patients showed symptomatic improvement. After 12 months, sIgG4 level demonstrated an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.867 for assessing SLIT as effective. Pre-treatment sIgG4 level showed an AUC of 0.869 for predicting SLIT as effective. Collectively, sIgG4 has strong potential assessing SLIT efficacy and prognosis in AR patients, with correlations to TNSS, TMS, VAS score, and IL-4, IL-10, IL-17, INF-γ, EOS% and sIgE levels.
Keywords: allergic rhinitis; specific immunoglobulin G4; sublingual immunotherapy; value of prognostic prediction; value of treatment efficacy assessment.
© 2024 The Author(s). The Kaohsiung Journal of Medical Sciences published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Kaohsiung Medical University.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
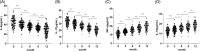

Similar articles
-
The Evaluation Value of the Modified Lund-Kennedy Nasal Endoscopy Score on the Efficacy of Sublingual Immunotherapy for Allergic Rhinitis.Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2024 Nov;38(6):366-372. doi: 10.1177/19458924241269786. Epub 2024 Aug 16. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2024. PMID: 39152637
-
[Effect of sublingual immunotherapy with Dermatophagoides Farinae on the expression of specific IgG4 in patients with allergic rhinitis in Hainan area].Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2020 Feb;34(2):135-139. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1001-1781.2020.02.009. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32086918 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
Changes in CD4+CD25+FoxP3+ Regulatory T Cells and Serum Cytokines in Sublingual and Subcutaneous Immunotherapy in Allergic Rhinitis with or without Asthma.Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2020;181(1):71-80. doi: 10.1159/000503143. Epub 2019 Nov 13. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2020. PMID: 31722337 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Specific sublingual immunotherapy in children with perennial rhinitis: a systemic review and meta-analysis.Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2020 Nov;10(11):1226-1235. doi: 10.1002/alr.22589. Epub 2020 Jun 25. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2020. PMID: 32329187
-
Specific immunotherapy for allergic rhinitis in children.Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2014 Dec;22(6):487-94. doi: 10.1097/MOO.0000000000000101. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2014. PMID: 25207858 Review.
References
-
- Bousquet J, Anto JM, Bachert C, Baiardini I, Bosnic‐Anticevich S, Walter Canonica G, et al. Allergic rhinitis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2020;6(1):95. - PubMed
-
- Gani F, Cottini M, Landi M, Berti A, Comberiati P, Peroni D, et al. Allergic rhinitis and COVID‐19: friends or foes? Eur Ann Allergy Clin Immunol. 2022;54(2):53–59. - PubMed
-
- Ricketti PA, Alandijani S, Lin CH, Casale TB. Investigational new drugs for allergic rhinitis. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2017;26(3):279–292. - PubMed
-
- Brozek JL, Bousquet J, Baena‐Cagnani CE, Bonini S, Canonica GW, Casale TB, et al. Allergic rhinitis and its impact on asthma (ARIA) guidelines: 2010 revision. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010;126(3):466–476. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

