Matched serum- and urine-derived biomarkers of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome
- PMID: 39739829
- PMCID: PMC11687793
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0309815
Matched serum- and urine-derived biomarkers of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome
Abstract
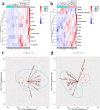
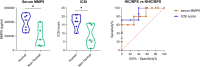
Setting up the correct diagnosis of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome (IC/BPS), a chronic inflammatory disease of the bladder, is a challenge, as there are neither diagnostic criteria nor reliable and non-invasive disease biomarkers available. The aim of the present study was to simultaneously determine matched serum- and urine-derived biomarkers of IC/BPS, which would provide additional insights into disease mechanisms and set the basis for further biomarker validation. Our study included 12 female patients with IC/BPS and 12 healthy controls. A total of 33 different biomarkers were measured, including cytokines and chemokines, proteins involved in extracellular matrix remodeling, adhesion molecules, growth factors, and markers of oxidative stress using enzyme linked immunoassays and multiplex technology. Heatmaps and principal component analysis based on significantly altered biomarkers, revealed urine- and serum-associated IC/BPS signatures that clearly differentiated IC/BPS patients from controls. Four biomarkers, including CCL11, BAFF, HGF and MMP9, were significantly upregulated in both serum and urine of patients with IC/BPS compared to controls. Serum levels of MMP9 were associated with disease severity and could distinguish well between IC/BPS patients with and without Hunner's lesions. Systemic levels of MMP9 can therefore mirror the local pathology within the bladders of IC/BPS patients, and MMP9 may prove to be a useful target for the development of novel therapeutic interventions. Utilizing a comprehensive panel of both urine and serum biomarkers, identified here, holds promise for disease detection in IC/BPS patients.
Copyright: © 2024 Kuret et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Philip Hanno MC, Myung Soo Choo J. Quentin Clemens, Ming-Huei Lee, Sachin Malde, Jane Meijlink, et al. Summary of the 2023 report of the international consultation on incontinence interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome (IC/BPS) committee. Continence. 2023;8(101056). doi: 10.1016/j.cont.2023.101056 - DOI
-
- Suskind AM, Berry SH, Ewing BA, Elliott MN, Suttorp MJ, Clemens JQ. The prevalence and overlap of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome and chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome in men: results of the RAND Interstitial Cystitis Epidemiology male study. J Urol. 2013;189(1):141–5. Epub 2012/11/21. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2012.08.088 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3894747. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Berry SH, Elliott MN, Suttorp M, Bogart LM, Stoto MA, Eggers P, et al. Prevalence of symptoms of bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis among adult females in the United States. J Urol. 2011;186(2):540–4. Epub 2011/06/21. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2011.03.132 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3513327. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

