Knowledge regarding human monkeypox among a sample of undergraduate and post-graduate students from selected tertiary institutions in Bangladesh: An online-based cross-sectional study
- PMID: 39739877
- PMCID: PMC11687903
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0315677
Knowledge regarding human monkeypox among a sample of undergraduate and post-graduate students from selected tertiary institutions in Bangladesh: An online-based cross-sectional study
Abstract
Background: The recent human monkeypox (mpox) outbreak in 2022 has become a serious concern due to its rapid expansion to various non-endemic countries. There is limited information about the knowledge regarding mpox among the Bangladeshi population. Therefore, this study's objectives were to: (i) determine the level of knowledge regarding mpox among undergraduate and post-graduate students in Bangladesh, and (ii) assess the determinants of knowledge regarding mpox among the study sample.
Methods: An online-based cross-sectional study was conducted among 879 tertiary-level students from selected tertiary institutions (n = 13) in Bangladesh. The structured questionnaire consisted of two parts: (i) socio-demographic information and (ii) an assessment of knowledge regarding mpox. The Kruskal-Wallis test, Mann-Whitney test, and multivariable quantile regression model were employed.
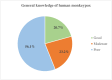
Results: The median age of the study participants was 23 years (IQR: 25-22). Low knowledge of mpox was found among study participants (20.7%, 23.2% and 56.1% had good, moderate and poor knowledge, respectively). The overall median knowledge score for mpox was 11 (IQR: 16-6). The median knowledge score of mpox significantly differed by participants' gender, study major, and academic education about mpox. In the quantile regression analysis, the association between gender and mpox knowledge was observed at the 25th (β = 1.343), 50th (β = 2.00) and 75th (β = 1.59) quantiles with females having more knowledge compared to males. The effects of study group were significant at 25th (β = 1.746), 50th (β = 1.5), 75th (β = 1.361) and 90th (β = 1.248) quantiles. Thus, those in medical or public health programs were likely to have more knowledge about mpox relative to those who were in non-medical related study groups. Students who received information about mpox during their education were more knowledgeable compared to those who had not, with statistical significance occurring at 10th (β = 3.711), 25th (β = 6.656), 50th (β = 5.75), 75th (β = 3.404) and 90th (β = 2.592) quantiles.
Conclusion: These findings imply that educational interventions about mpox should consider the gender dynamics and program of study among the students in Bangladesh.
Copyright: © 2024 Banna et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Alrasheedy AA, Aldawsari AH, Alqasir MI, Alsawyan OA, Alalwan OA, Alwaker SA, et al. Knowledge of Community Pharmacists in Saudi Arabia Regarding Human Monkeypox, Its Management, Prevention, and Vaccination: Findings and Implications. Vaccines. 2023;11: 878. doi: 10.3390/vaccines11040878 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical