Exploring determinant factors influencing muscle quality and sarcopenia in Bilbao's older adult population through machine learning: A comprehensive analysis approach
- PMID: 39739941
- PMCID: PMC11687929
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0316174
Exploring determinant factors influencing muscle quality and sarcopenia in Bilbao's older adult population through machine learning: A comprehensive analysis approach
Abstract
Background: Sarcopenia and reduced muscle quality index have garnered special attention due to their prevalence among older individuals and the adverse effects they generate. Early detection of these geriatric pathologies holds significant potential, enabling the implementation of interventions that may slow or reverse their progression, thereby improving the individual's overall health and quality of life. In this context, artificial intelligence opens up new opportunities to identify the key identifying factors of these pathologies, thus facilitating earlier intervention and personalized treatment approaches.
Objectives: investigate anthropomorphic, functional, and socioeconomic factors associated with muscle quality and sarcopenia using machine learning approaches and identify key determinant factors for their potential future integration into clinical practice.
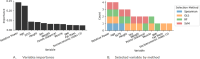
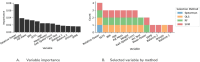
Methods: A total of 1253 older adults (89.5% women) with a mean age of 78.13 ± 5.78 voluntarily participated in this descriptive cross-sectional study, which examines determining factors in sarcopenia and MQI using machine learning techniques. Feature selection was completed using a variety of techniques and feature datasets were constructed according to feature selection. Three machine learning classification algorithms classified sarcopenia and MQI in each dataset, and the performance of classification models was compared.
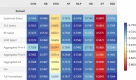
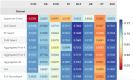
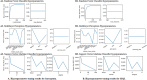
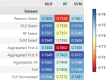
Results: The predictive models used in this study exhibited AUC scores of 0.7671 for MQI and 0.7649 for sarcopenia, with the most successful algorithms being SVM and MLP. Key factors in predicting both conditions have been shown to be relative power, age, weight, and the 5STS. No single factor is sufficient to predict either condition, and by comprehensively considering all selected features, the study underscores the importance of a holistic approach in understanding and addressing sarcopenia and MQI among older adults.
Conclusions: Exploring the factors that affect sarcopenia and MQI in older adults, this study highlights that relative power, age, weight, and the 5STS are significant determinants. While considering these clinical markers and using a holistic approach, this can provide crucial information for designing personalized and effective interventions to promote healthy aging.
Copyright: © 2024 Virto et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

