Differential contribution of PBP occupancy and efflux on the effectiveness of β-lactams at their target site in clinical isolates of Neisseria gonorrhoeae
- PMID: 39739989
- PMCID: PMC11729944
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1012783
Differential contribution of PBP occupancy and efflux on the effectiveness of β-lactams at their target site in clinical isolates of Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Abstract
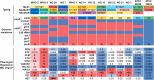
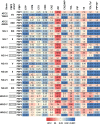
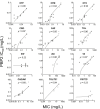
Neisseria gonorrhoeae exhibits alarming antibiotic resistance trends and poses a significant challenge in therapeutic management. This study aimed to explore the association of penA alleles with penicillin-binding protein (PBP) occupancy patterns and reduced outer membrane permeability, impacting susceptibility to last-line cephalosporins and potential β-lactam candidates. The whole genome sequence, the MICs and PBP IC50s were determined for 12 β-lactams and β-lactamase inhibitors in 8 clinical isolates with varying β-lactam sensitivity, 2 ATCC, and 3 WHO cephalosporin-resistant reference strains. The genetic analysis identified diverse determinants of β-lactam resistance including penA, ponA, porB, and mtrR alterations. Mosaic penA alleles were confirmed to be key determinants of cephalosporin resistance, with notable impacts on PBP2 IC50 affinities (in the presence of all PBPs). Substitutions in positions V316 and A501 exhibited significant effects on β-lactam PBP2 occupancy and MICs. PBP1 inhibition showed marginal effect on β-lactam sensitivity and PBP3 acted as a sink target. Ertapenem and piperacillin emerged as potential therapies against cephalosporin-resistant N. gonorrhoeae strains, along with combination therapies involving tazobactam and/or efflux inhibitors. The study determined the β-lactam PBP-binding affinities of last-line cephalosporins and alternative β-lactam candidates in strains carrying different penA alleles for the first time. These findings provide insights for developing new antimicrobial agents and enhancers against emerging resistant strains. Further research is warranted to optimize therapeutic interventions for cephalosporin-resistant N. gonorrhoeae infections.
Copyright: © 2024 López-Argüello et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
AO has received fees as speaker and/or research grants from MSD, Pfizer and Wockhardt.
Figures
References
-
- Salmerón P, Viñado B, Arando M, Alcoceba E, Romero B, Menéndez B, et al. Neisseria gonorrhoeaeNeisseria gonorrhoeae antimicrobial resistance in Spain: a prospective multicentre study. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2021;76(6):1523–31. - PubMed
-
- ECDC. Sexually transmitted infections in Europe. 2023.
-
- Cámara J, Serra J, Ayats J, Bastida T, Carnicer-Pont D, Andreu A, et al. Molecular characterization of two high-level ceftriaxone-resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeaeNeisseria gonorrhoeae isolates detected in Catalonia, Spain. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2012;67(8):1858–60. - PubMed
-
- Tapsall JW, Ndowa F, Lewis DA, Unemo M. Meeting the public health challenge of multidrug- and extensively drug-resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2009;7(7):821–34. - PubMed
-
- Ohnishi M, Golparian D, Shimuta K, Saika T, Hoshina S, Iwasaku K, et al. Is Neisseria gonorrhoeaeNeisseria gonorrhoeae initiating a future era of untreatable gonorrhea?: detailed characterization of the first strain with high-level resistance to ceftriaxone. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011;55(7):3538–45. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

