Recommendations on Ultrasound-Guided Hyaluronic Acid Soft Tissue Augmentation of the Upper Face in Asians
- PMID: 39740068
- PMCID: PMC11684153
- DOI: 10.1111/jocd.16759
Recommendations on Ultrasound-Guided Hyaluronic Acid Soft Tissue Augmentation of the Upper Face in Asians
Abstract
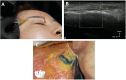
Background: Ultrasonography allows real-time imaging of facial soft tissue during hyaluronic acid (HA) filler injections. However, there is currently limited guidance relating to ultrasound-guided HA filler placement in the upper face.
Aims: To develop guidance for the effective use of ultrasonography to improve the safety of HA filler injection procedures.
Methods: Through a series of online video conferences and anatomical studies conducted on a model and a cadaveric specimen, specialists from Korea, Thailand, and China drew recommendations for ultrasound-guided filler injections of the upper face.
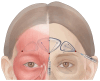
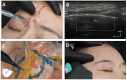
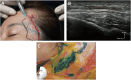
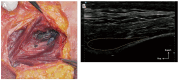
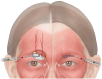
Results: The authors outlined critical anatomical landmarks for safe HA filler placement to correct volume deficits or treat hollowness of the forehead, temple, and upper eyelids. They provide insights on treatment indications and injection techniques using ultrasound for safe HA filler placement. The recommendations are presented in this paper.
Conclusions: Where there are anatomic variations in the vasculature of the forehead, temple, and periorbital area, ultrasound-guided filler placement can provide an additional safety measure. Current evidence may give rise to standard practices incorporating ultrasound in injection protocols for the preventive and therapeutic management of adverse events.
Keywords: forehead; hyaluronic acid filler; injection; temple; ultrasonography; upper eyelid.
© 2024 The Author(s). Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
Beyond this study, J.Y.J., H.C., S.C.H., R.W., Q.L., L.Z., and H‐.J.K. declare no conflicts of interest. J.I.N. and W.E.J. are full‐time employees of LG Chem Co. Ltd.
Figures


References
-
- Signorini M., Liew S., Sundaram H., et al., “Global Aesthetics Consensus: Avoidance and Management of Complications From Hyaluronic Acid Fillers‐Evidence‐ and Opinion‐Based Review and Consensus Recommendations,” Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery 137, no. 6 (2016): 961e–971e, 10.1097/PRS.0000000000002184. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

