Clonal GZMK+CD8+ T cells are identified as a hallmark of the pathogenesis of cGVHD-induced bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
- PMID: 39740295
- PMCID: PMC11750515
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2024.105535
Clonal GZMK+CD8+ T cells are identified as a hallmark of the pathogenesis of cGVHD-induced bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
Abstract
Background: Bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome (BOS) is one of the most devastating outcomes of chronic graft-versus-host disease (cGVHD) after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (allo-HSCT). This remains an area of unmet clinical need for optimal therapy for BOS patients partly due to the limited understanding of pathogenic mechanisms.
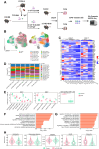
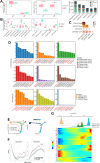
Methods: We collected blood samples from 22 patients with cGVHD and 11 patients without cGVHD following allo-HSCT. By applying a combination of mass cytometry (CyTOF), RNA-sequencing and the quantitative cytokine array, we discovered a new cellular hallmarker of patients with cGVHD-BOS. This finding was further validated in cGVHD-BOS murine models by using single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) and paired single-cell V(D)J sequencing analyses.
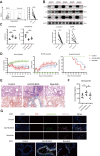
Findings: We revealed that circulating Granzyme K (GZMK)-expressing CD8+ T cells with increased expression of CCR5 were accumulated in cGVHD-BOS patients, and GZMK can induce the expression of fibrosis-essential proteins, collagen type I alpha 1 chain (COL1A1) and fibronectin (FN1), in human fibroblasts. As compared to those of control mice, GZMK+CD8+ T cells in the lungs of cGVHD-BOS mice were undergoing significant infiltration and clonal hyperexpansion, with more cytotoxic, pro-inflammatory, migratory and exhausted phenotypes. Moreover, we screened small-molecule drugs and revealed that Bosutinib, the second-generation BCR-ABL1-targeting tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI), could inhibit GZMK expression in CD8+ T cells and reduce lung stiffness and pulmonary fibrosis in cGVHD-BOS mice.
Interpretation: This study provides proof-of-principle evidence for clonal GZMK+CD8+ T cells as an unexplored contributor to the pathogenesis of cGVHD-BOS, which can be an underlying biomarker for treatment.
Funding: This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82170141, 82100123, 81870136), and "Pioneer" and "Leading Goose" R&D Program of Zhejiang (grant No. 2022C03012).
Keywords: Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation; Bosutinib; Bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome; Chronic graft-versus-host disease; Granzyme K.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Remberger M., Beelen D.W., Fauser A., Basara N., Basu O., Ringden O. Increased risk of extensive chronic graft-versus-host disease after allogeneic peripheral blood stem cell transplantation using unrelated donors. Blood. 2005;105(2):548–551. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

