A Neural Circuit From Paraventricular Nucleus of the Thalamus to the Nucleus Accumbens Mediates Inflammatory Pain in Mice
- PMID: 39740781
- PMCID: PMC11688111
- DOI: 10.1002/brb3.70218
A Neural Circuit From Paraventricular Nucleus of the Thalamus to the Nucleus Accumbens Mediates Inflammatory Pain in Mice
Abstract
Background: Pain is a prevalent comorbidity in numerous clinical conditions and causes suffering; however, the mechanism of pain is intricate, and the neural circuitry underlying pain in the brain remains incompletely elucidated. More research into the perception and modulation of pain within the central nervous system is essential. The nucleus accumbens (NAc) plays a pivotal role in the regulation of animal behavior, and extensive research has unequivocally demonstrated its significant involvement in the occurrence and development of pain. NAc receives projections from various other neural nuclei within the brain, including the paraventricular nucleus of the thalamus (PVT). In this experiment, we demonstrate that the specific glutamatergic neural circuit projection from PVT to NAc (PVTGlut→NAc) is implicated in the modulation of inflammatory pain in mice.
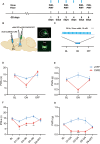
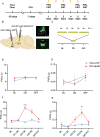
Methods: We compared the difference in pain thresholds between complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA)-induced inflammatory pain models and controls. Then in a well-established mouse model of CFA-induced inflammatory pain, immunofluorescence staining was utilized to evaluate changes in c-Fos protein expression within PVT neurons. To investigate the role of PVTGlut→NAc in the modulation of pain, we used optogenetics to modulate this neural circuit, and nociceptive behavioral tests were employed to investigate the functional role of the PVTGlut→NAc circuit in the modulation of inflammatory pain.
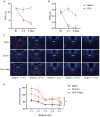
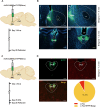
Results: In the mice with the inflammatory pain group, both the paw withdrawal latencies (PWLs) and paw withdrawal thresholds (PWTs) of the right hind paw were decreased compared to the control group. In addition, compared to the control group, CFA-induced inflammatory pain led to increased c-Fos protein expression in PVT, which means that some of the neurons in this area of the brain region have been activated. Following the injection of retrograde transport fluorescent-labeled virus into NAc, glutamatergic neurons projecting from the PVT to NAc were observed, confirming the projection relationship between PVT and NAc. In the experiments in optogenetic regulation, normal mice exhibited pain behavior when the PVTGlut→NAc circuit was stimulated by a 473 nm blue laser, resulting in decreased PWLs and PWTs compared to the control group, which means activating this neural circuit can lead to painful behaviors. In the CFA-induced pain group, inhibition of the PVTGlut→NAc circuit by a 589 nm yellow laser alleviated pain behavior, leading to increased PWLs and PWTs compared to the control group, representing the fact that inhibition of this neural circuit relieves pain behaviors.
Conclusions: The findings unveil a pivotal role of the PVTGlut→NAc circuit in modulating inflammatory pain induced by CFA in mice.
Keywords: inflammatory pain; nucleus accumbens; optogenetics; paraventricular nucleus of the thalamus.
© 2024 The Author(s). Brain and Behavior published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 82171227/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81300957/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- LY22H090019/Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province
- LY21H090001/Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province
- 202311KFY00102/Open project fund of the Key Laboratory for NeuroInformation of Ministry of Education
- Zhejiang Province Cerebrovascular Disease Diagnosis and Treatment of traditional Chinese Medicine Multidisciplinary Innovation Team Project
- "Integration of Medicine, Industry and information" Collaborative Innovation Center Fund of Yangtze Delta Region Institute (Huzhou), University of Electronic Science and Technology of China-Huzhou Central Hospital
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

