The Combination of Tumor-targeting Salmonella typhimurium A1-R Plus the Autophagy-inhibitor Chloroquine Synergistically Eradicates HT1080 Fibrosarcoma Cells In Vitro and In Vivo
- PMID: 39740880
- PMCID: PMC11705149
- DOI: 10.21873/invivo.13807
The Combination of Tumor-targeting Salmonella typhimurium A1-R Plus the Autophagy-inhibitor Chloroquine Synergistically Eradicates HT1080 Fibrosarcoma Cells In Vitro and In Vivo
Abstract
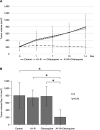
Background/aim: Salmonella typhimurium A1-R (A1-R) targets and inhibits a wide range of cancer types without continuously infecting healthy tissue. Chloroquine, an antimalarial drug, induces apoptosis and inhibits autophagy in cancer cells. The aim of the present study was to determine the synergy of A1-R plus chloroquine on HT1080 human fibrosarcoma cells in vitro and in a nude-mouse model.
Materials and methods: HT1080 human fibrosarcoma cells were used for in vitro experiments. Four groups were analysed in vitro: No-treatment control; A1-R; chloroquine; A1-R plus chloroquine. The nude-mouse models of HT1080 human fibrosarcoma were randomly assigned into four groups: G1: untreated control; G2: Oral A1-R [5×107 colony forming units (CFU)/body, twice a week, 2 weeks]; G3: Chloroquine [100 mg/kg/body, intraperitoneal (IP) administration, twice a week, 2 weeks]; G4: Oral A1-R (5×107 CFU/body), twice a week, 2 weeks plus chloroquine (100 mg/kg/body, IP), twice a week, 2 weeks. Each cohort consisted of five mice. Tumor volume and body weight were assessed biweekly.
Results: A1-R combined with chloroquine synergistically decreased the viability of HT1080 cells in vitro compared to other groups. Orally-administered A1-R at 5×107 CFU combined with IP-administered chloroquine eradicated HT1080 tumors in nude mice, without body-weight decrease.
Conclusion: The combination treatment of A1-R plus chloroquine demonstrated synergy against HT1080 cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. A1-R was administered orally, suggesting its potential as a probiotic. The present results suggest the clinical potential of the combination of A1-R and chloroquine for soft-tissue sarcoma therapy, a recalcitrant disease.
Keywords: Salmonella typhimurium A1-R; autophagy-inhibitor; chloroquine; combination; fibrosarcoma; nude mice; oral administration; synergy HT1080; tumor eradication.
Copyright © 2025, International Institute of Anticancer Research (Dr. George J. Delinasios), All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The Authors declare no competing interests in relation to this study.
Figures




References
-
- Zhang Y, Tome Y, Suetsugu A, Zhang L, Zhang N, Hoffman RM, Zhao M. Determination of the optimal route of administration of Salmonella typhimurium A1-R to target breast cancer in nude mice. Anticancer Res. 2012;32:2501–2508. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
