Impaired coagulation parameters in early RA are restored by effective antirheumatic therapy: a prospective pilot study
- PMID: 39740931
- PMCID: PMC11748942
- DOI: 10.1136/rmdopen-2024-004838
Impaired coagulation parameters in early RA are restored by effective antirheumatic therapy: a prospective pilot study
Abstract
Objectives: To assess the effect of treatment on haemostatic parameters in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Methods: Patients with newly diagnosed RA started methotrexate and were randomised to additional conventional treatment, certolizumab pegol, abatacept or tocilizumab. Several biomarkers for haemostasis were analysed including parameters of the two global haemostatic assays-overall haemostatic potential (OHP) and endogenous thrombin potential (ETP), as well as single haemostatic factors-fibrinogen, prothrombin fragment 1+2 (F1+2), D-dimer, thrombin activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor (TAFI) and clot lysis time (CLT) in 24 patients at baseline, 12 and 24 weeks after the start of the treatment.
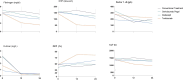
Results: At baseline, patients had elevated levels of the following biomarkers compared with reference values: fibrinogen, F1+2, D-dimer and parameters of the two global haemostatic assays, that is, ETP and OHP. After 24 weeks we observed a significant reduction in F1+2 (p<0.01), fibrinogen (p<0.01), D-dimer (p<0.01), OHP (p<0.01), ETP (p<0.01), CLT (p<0.01), TAFI (p<0.01) and an increase of OFP (p<0.01). Tocilizumab treatment resulted in the most significant reduction of global haemostatic assays after 24 weeks, that is, a reduction of OHP 73% (p<0.01) compared with certolizumab pegol arm 32% (p<0.01), abatacept arm 24% (p=0.25) or conventional treatment arm 7% (p=0.66).
Conclusion: Newly diagnosed RA patients have enhanced coagulation activation and impaired fibrinolysis as demonstrated by our results. Effective antirheumatic treatments during the first 24 weeks after diagnosis improved this haemostatic imbalance, with prominent effects of biological drugs and especially tocilizumab, compared with conventional treatment.
Keywords: Arthritis, Rheumatoid; Biological Therapy; Cardiovascular Diseases; Treatment.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2024. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: BD has received consulting fees from Galapagos and Novartis. DCN received consulting fees from AbbVie, BMS, Lilly, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche and UCB' meeting support from Pfizer; advisory board participation fee from Novartis; and other service fee by BMS. MTN received research grants from AbbVie, BMS, Pfizer, Galapagos, Amgen and Eli Lily. BG received consulting fee from Novartis and honorary lecture payment from Novartis and Nordic-Pharma. BG received consulting fee from Novartis and honorary lecture payment from Novartis and Nordic-Pharma. MLH received research grants from AbbVie, Biogen, BMS, Celtrion, Eli Lily, Janssen Biologics B.V., Lundbeck Foundation, MSD, Pfizer, Roche, Samsung Biopies, Sandoz and Novartis; and institution pay from Pfizer, Medac, AbbVie and Sandoz; chaired the steering committee of the Danish Rheumatology Quality Registry (DANBIO), which receives public funding from the hospital owners and funding from pharmaceutical companies; cochairs EuroSpA, which generates real-world evidence of treatment of psoriatic arthritis and axial spondylorthritis based on secondary data and is partly funded by Novartis. MØ received the study drug from BMS and UCB; research grants from Abbvie, BMS, Merck, Novartis and UCB; speaker fees from Abbvie, BMS, Celgene, Eli-Lilly, Galapagos, Gilead, Janssen, MEDAC, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, Sandoz, and UCB; and consultancy fees from Abbvie, BMS, Celgene, Eli-Lilly, Galapagos, Gilead, Janssen, MEDAC, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, Sandoz and UCB. RFvV received the study drug from BMS and UCB; research grants from BMS, GSK, UCB and AstraZeneca; consulting fees from AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Biogen, BMS, Galapagos, Janssen, Miltenyi, Pfizer and UCB; expert fees from AbbVie, Galapagos, GSK, Janssen, Pfizer, R-Pharma and UCB; and advisory board fees from AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Biogen, BMS, Galapagos, Janssen, Miltenyi, Pfizer and UCB. MTN received research grants from AbbVie, BMS, Pfizer, Galapagos, Amgen and Eli Lily. BG received consulting fee from Novartis and honorary lecture payment from Novartis and Nordic-Pharma. The remaining authors declared no disclosures.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical