Induction of interleukin 21 receptor expression via enhanced intracellular metabolism in B cells and its relevance to the disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus
- PMID: 39740932
- PMCID: PMC11749818
- DOI: 10.1136/rmdopen-2024-004567
Induction of interleukin 21 receptor expression via enhanced intracellular metabolism in B cells and its relevance to the disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus
Abstract
Objective: To elucidate the association between the changes in intracellular metabolism in the early stage of B cell activation and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) pathogenesis.
Methods: CD19+ or CD19+CD27- (naïve) cells from the peripheral blood of healthy controls and lupus patients were cultured under different stimuli. The changes in intracellular metabolism and signalling pathways in these cells were evaluated.
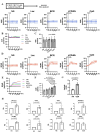
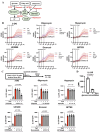
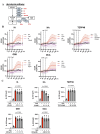
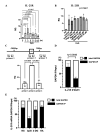
Results: Stimulation with CpG (Toll-like receptor 9 (TLR9) ligand) in vitro induced enhanced interleukin 21 (IL-21) receptor expression in CD19+CD27- cells after 24 hours. The addition of IL-21 to the CpG stimulation enhanced the extracellular acidification rate, which indicates glycolysis, within 30 min. IL-21 receptor (IL-21R) expression induced by CpG stimulation was selectively inhibited by 2-deoxy-D-glucose (hexokinase 2 (HK2) inhibitor) and heptelidic acid (glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) inhibitor). RNA immunoprecipitation with anti-GAPDH antibody revealed that CpG stimulation dissociated the binding between IL-21R messenger RNA (mRNA) and GAPDH under no stimulation. HK2 and GAPDH expression were higher in CD19+CD27- cells of lupus patients than in those of healthy controls, and GAPDH expression was correlated with the plasmocyte count and disease activity score.
Conclusion: IL-21R mRNA-GAPDH binding dissociation associated with rapid glycolytic enhancement by the TLR9 ligand in B cells may induce plasmocyte differentiation through IL-21 signals and be involved in exacerbating SLE.
Keywords: Autoimmune Diseases; Immune System Diseases; Lupus Erythematosus, Systemic.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2024. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ Group.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: MU has received speaking fee and honoraria from GlaxoSmithKline. SI has received consulting fees, speaking fees and honoraria from Ono, Taisho, Janssen, UCB, AstraZeneca, Pfizer, GlaxoSmithKline, Astellas, Asahi Kasei, Teijin, Eli Lilly, Nippon-Shinyaku, Daiichi-Sankyo, AbbVie, Eisai, Mitsubishi-Tanabe and Chugai. KS has received speaking fee from Chugai, Astellas, AbbVie, Taisho, Janssen, Eli Lilly Japan, Ayumi and Gilead Sciences and has received research funding from UCB Japan. SK has received consulting fees, speaking fees and honoraria from Eli Lilly, Bristol-Myers and GlaxoSmithKline and has received research grants from Daiichi-Sankyo, AbbVie, Behringer-Ingelheim and Astellas. YM has received consulting fees, speaking fees and honoraria from Eli Lilly and has received research grants from GlaxoSmithKline. SN has received consulting fees, speaking fees, lecture fees and/or honoraria from AstraZeneca, GlaxoSmithKline, Pfizer, Bristol-Myers, Astellas, Asahi Kasei, AbbVie, Chugai, Sanofi, Eisai, Gilead Sciences, Mitsubishi-Tanabe, Janssen, Eli Lilly and Ayumi. YT has received consulting fees, speaking fees and honoraria from Behringer-Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, AbbVie, Gilead, AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers, Chugai, Daiichi-Sankyo, Eisai, Pfizer, Mitsubishi-Tanabe and GlaxoSmithKline and has received research grants from Asahi Kasei, AbbVie, Chugai, Eisai, Takeda, Daiichi-Sankyo and Behringer-Ingelheim.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
