Biomarkers reflecting disturbed gut barrier under treatment with TNF inhibitors in radiographic axial spondyloarthritis
- PMID: 39740933
- PMCID: PMC11749320
- DOI: 10.1136/rmdopen-2024-004752
Biomarkers reflecting disturbed gut barrier under treatment with TNF inhibitors in radiographic axial spondyloarthritis
Abstract
Objectives: The objective of this study is to investigate lipopolysaccharid-binding protein (LBP), zonulin and calprotectin as markers of bacterial translocation, disturbed gut barrier and intestinal inflammation in patients with radiographic axial spondyloarthritis (r-axSpA) during tumour necrosis factor inhibitor (TNFi) therapy and to analyze the association between disease activity, response to treatment and biomarker levels.
Methods: Patients with active r-axSpA of the German Spondyloarthritis Inception Cohort starting TNFi were compared with controls with chronic back pain. Serum levels of LBP, zonulin and calprotectin were measured at baseline and after 1 year of TNFi therapy. We analysed the longitudinal association between biomarkers and disease activity, and the relationship between biomarkers and treatment response with regression analysis.
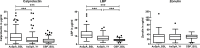
Results: 121 patients with r-axSpA were compared with 63 controls. At baseline, patients with r-axSpA had higher levels of LBP and calprotectin than controls, which decreased significantly during TNFi treatment. LBP showed a positive association in longitudinal analyses with Axial Spondyloarthritis Disease Activity Score (ASDAS) (ß=0.08, 95% CI 0.06 to 0.10), Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (BASDAI) (ß=0.08, 95% CI 0.04 to 0.12) and C reactive protein (CRP) (ß=1.69, 95% CI 1.04 to 2.34). Calprotectin was associated with ASDAS (ß=0.04, 95% CI 0.01 to 0.07) and CRP (ß=0.82, 95% CI 0.27 to 1.37). Furthermore, LBP and calprotectin levels at baseline showed an association with a subsequent change in BASDAI. Baseline zonulin levels were not significantly associated with disease activity or treatment response.
Conclusion: Serum levels of LBP and calprotectin are associated with disease activity in patients with r-axSpA and decrease with TNFi response. In contrast, serum zonulin levels showed no association with disease activity or treatment response, arguing against a strict correlation between intestinal permeability and disease activity in axSpA.
Keywords: Axial Spondyloarthritis; Spondylitis, Ankylosing; Tumor Necrosis Factor Inhibitors.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2024. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ Group.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: JR declares support for attending meetings and/or travel from AbbVie, Novartis, and Janssen; and payment for presentations from Janssen outside the presented work. FP discloses research support from Eli Lilly, Novartis and UCB; Consultancy fees and speaker bureau from AbbVie, Amgen, BMS, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Galapagos, Hexal, Janssen, Medscape, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche and UCB. HH reports grants or contracts from Sobi, consulting fees from Abbvie, Janssen, Novartis, Sobi, UCB, Pfizer, Roche and payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speakers bureaus, manuscript writing or educational events from Abbvie, Janssen, Novartis, Sobi, UCB, Pfizer, Roche as well as support for attending meetings and/or travel from Novartis, AbbVie and UCB. MP has received honoraria from Novartis and Janssen, and other financial/material support from Abbvie and UCB. LS reports support for attending meetings and/or travel from AbbVie and MSD. DP reports grants and personal fees from AbbVie, Eli Lilly, MSD, Novartis and Pfizer, and personal fees from Bristol-Myers Squibb, Janssen, UCB, Biocad, GlaxoSmithKline, Galapagos, Gilead, Moonlake, Medscape, Peervoice and Samsung Bioepis outside the presented work. VRR reports personal fees from AbbVie, Falk, Takeda and support for attending meetings and/or travel from Pfizer and Novartis outside the presented work. MT and CMH have nothing to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Ørnbjerg LM, Brahe CH, Askling J, et al. Treatment response and drug retention rates in 24 195 biologic-naïve patients with axial spondyloarthritis initiating TNFi treatment: routine care data from 12 registries in the EuroSpA collaboration. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019;78:1536–44. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-215427. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
