Benzoylaconine: Potential Therapeutic Agent for Cardiovascular Diseases From Fuzi
- PMID: 39742007
- PMCID: PMC11236470
- DOI: 10.1155/2024/4878103
Benzoylaconine: Potential Therapeutic Agent for Cardiovascular Diseases From Fuzi
Abstract
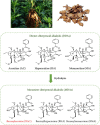
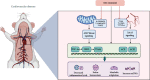
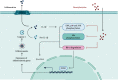
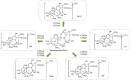
Modern pharmacological studies have elucidated the presence of aconitine (AC) alkaloids, polysaccharides, and saponins as the primary bioactive constituents of Fuzi. Among these, benzoylaconine, a pivotal active compound, demonstrates notable pharmacological properties including antitumor, anti-inflammatory, and cardiovascular protective effects. In recent years, benzoylaconine has garnered significant attention in basic research on heart diseases, emerging as a focal point of investigation. This paper presents a comprehensive review of the pharmacological effects of benzoylaconine, alongside an overview of advancements in metabolic characterization. The objective is to furnish valuable insights that can serve as a cornerstone for further exploration, utilization, and advancement of benzoylaconine in pharmacological research.
Keywords: anti-inflammation; benzoylaconine; cardiac diseases; pharmacokinetics; pharmacological effects.
Copyright © 2024 Chenggang Xu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Committee for the pharmacopoeia of China. Pharmacopoeia of China, Part I . Beijing: China Medical Science and Technology Press; 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources