Discovery and Validation of Potential Serum Biomarkers for Heart Failure by Untargeted Metabolomics
- PMID: 39742011
- PMCID: PMC11338663
- DOI: 10.1155/2024/7004371
Discovery and Validation of Potential Serum Biomarkers for Heart Failure by Untargeted Metabolomics
Abstract
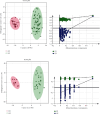
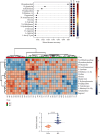
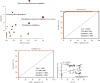
Detection of biomarkers was extremely important for the early diagnosis, prognosis, and therapy optimization of diseases. The purpose of this study was to investigate the differences in serum metabolites between patients with heart failure (HF) and healthy control (HC) and to diagnose HF qualitatively. In this study, serum samples from 83 patients with HF and 35 HCs were used as the research subjects for untargeted metabolomic analysis using ultraperformance liquid chromatography combined with quadrupole-time of flight mass spectrometry (UPLC-QTOF/MS) technology. Potential biomarkers were screened and validated using the orthogonal partial least squares discriminant analysis (OPLS-DA), random forest (RF), binary logistic regression (BLR), and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis. The results indicated that a total of 43 metabolites were considered as differentially expressed metabolites (DEMs). Among these DEMs, glycodeoxycholate was identified as a specific biomarker of HF. A ROC curve analysis for HC versus HF discrimination showed an area under the ROC curve (AUC) of 0.9853 (95% CI: 0.9859-1.0000), a sensitivity of 95%, and a specificity of 100%. Hence, glycodeoxycholate might serve as a potential biomarker for HF. Furthermore, the amino acid metabolism was screened as the most significantly altered pathway in patients with HF. By identifying serum biomarkers and analyzing metabolic pathways, our study provided opportunities to enhance the understanding of the pathogenesis and early diagnosis of HF.
Keywords: UPLC/Q-TOF-MS; biomarker; heart failure; metabolite profile; serum metabolomics.
Copyright © 2024 Guisheng Zhou et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

