Attenuating Atherosclerosis through Inhibition of the NF- κ B/NLRP3/IL-1 β Pathway-Mediated Pyroptosis in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells (VSMCs)
- PMID: 39742016
- PMCID: PMC10985643
- DOI: 10.1155/2024/1506083
Attenuating Atherosclerosis through Inhibition of the NF- κ B/NLRP3/IL-1 β Pathway-Mediated Pyroptosis in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells (VSMCs)
Abstract
Objective: We investigated the effects of resveratrol (Res) and MCC950 on the pyroptosis of vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) and the potential pathway.
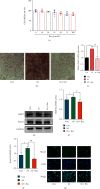
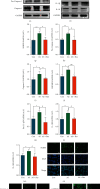
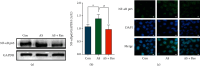
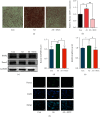
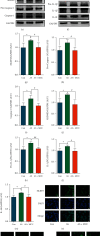
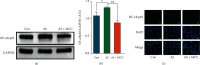
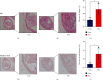
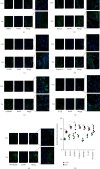
Methods and results: Compared with the control (Con) group, the atherosclerosis (AS) group showed calcified nodules, which suggested that the calcification medium induced the calcification of VSMCs. VSMCs showed proliferative activity and significantly attenuated calcification under treatment with 10 μmol/L Res. The calcium salt was detected by alizarin red S staining. Res and MCC950 downregulated the calcification, inflammatory, pyroptosis, and transcription factor-related indicators all decreased by RT-qPCR with Western blot and immunofluorescence. The results showed that Res and MCC950 refrained the calcification of VSMCs and that Res has a better effect than MCC950. Plaques and calcium salt deposits were present in the carotid region in the control group. More calcium salt deposits were evident in the plaques of the Par group by HE staining and alizarin red S staining. The calcification indexes BMP2, Runx2, and related indexes declined by immunofluorescence, which showed parthenolide-inhibited AS. The related protein expressions were consistent with the expression of the cell experiments.
Conclusion: Our data demonstrated that inflammatory response and pyroptosis exacerbate AS and unravel the link between VSMCs and the progression of AS lesions. Res and MCC950 inhibited the calcification of VSMCs by regulating NF-κB/NLRP3/IL-1β signaling axis. P53 can exacerbate the AS lesions by acting on NLRP3 inflammasome and pyroptosis. Our findings supported the clinical applications of Res and MCC950 in VSMCs individuals to counteract pyroptosis and AS, and P53 inhibitors also can be a potential treatment for AS.
Copyright © 2024 Shihuan Li et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- AlSiraj Y., Thatcher S. E., Liang C. L., Ali H., Ensor M., Cassis L. A. Therapeutic assessment of combination therapy with a neprilysin inhibitor and angiotensin type 1 receptor antagonist on angiotensin II-induced atherosclerosis, abdominal aortic aneurysms, and hypertension. The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics . 2021;377(3):326–335. doi: 10.1124/jpet.121.000525. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

