Advances in the isolation and characterization of milk-derived extracellular vesicles and their functions
- PMID: 39742102
- PMCID: PMC11688093
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1512939
Advances in the isolation and characterization of milk-derived extracellular vesicles and their functions
Abstract
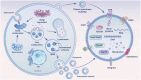
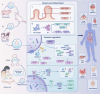
Milk-derived extracellular vesicles (EVs) have various functions, including immune regulation and promoting intestinal development. These EVs have substantial potential for application in infant formula and functional foods development. In addition, numerous studies have shown that milk-derived EVs carry proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids away from their parental cells, acting as messengers between cells. Moreover, structural integrity and biological viability are necessary prerequisites for the functional and omics studies of milk-derived EVs. Therefore, selecting appropriate methods for isolating and characterizing milk-derived EVs is essential for subsequent studies. Accordingly, this review summarizes the isolation and characterization methods for milk-derived EVs and their biological functions and roles. Furthermore, it discusses the comprehensive application of isolation methods, providing a reference for research on and development of milk-derived EVs.
Keywords: biological functions; characterization; extracellular vesicles; infant; isolation methods; milk.
Copyright © 2024 Di, Huang, Qiao, Zhang, Wang, Zhang, Fu, Zhao and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
SD, YH, WQ, XZ, YW, MZ, JF, JZ, LC were employed by Beijing Sanyuan Foods Co. Ltd.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Biological Properties of Milk-Derived Extracellular Vesicles and Their Physiological Functions in Infant.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Jun 25;9:693534. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.693534. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34249944 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Isolation and Characterization of Cow-, Buffalo-, Sheep- and Goat-Milk-Derived Extracellular Vesicles.Cells. 2023 Oct 20;12(20):2491. doi: 10.3390/cells12202491. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37887335 Free PMC article.
-
Flood Control: How Milk-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Can Help to Improve the Intestinal Barrier Function and Break the Gut-Joint Axis in Rheumatoid Arthritis.Front Immunol. 2021 Jul 28;12:703277. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.703277. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34394100 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Key roles of milk-derived extracellular vesicles in intestinal tract, with special emphasis on microRNAs in extracellular vesicles.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2025 Mar 6:1-23. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2025.2473623. Online ahead of print. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40047253 Review.
-
Milk-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Inter-Organism, Cross-Species Communication and Drug Delivery.Proteomes. 2020 May 13;8(2):11. doi: 10.3390/proteomes8020011. Proteomes. 2020. PMID: 32414045 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Microneedle loaded with luteolin-colostrum-derived exosomes: a dropless approach for treatment of glaucoma.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2025 Jul 11. doi: 10.1007/s13346-025-01914-9. Online ahead of print. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2025. PMID: 40643885
-
RNAi delivery mediated by milk extracellular vesicles in colon cancer.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2025 Jul 31;36(3):102644. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2025.102644. eCollection 2025 Sep 9. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2025. PMID: 40896585 Free PMC article.
-
Camel Milk-Derived Extracellular Vesicles as a Functional Food Component Ameliorate Hypobaric Hypoxia-Induced Colonic Injury Through Microbiota-Metabolite Crosstalk.Nutrients. 2025 Jul 25;17(15):2431. doi: 10.3390/nu17152431. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40806022 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

