Deep Learning-Based Carotid Plaque Ultrasound Image Detection and Classification Study
- PMID: 39742249
- PMCID: PMC11683696
- DOI: 10.31083/j.rcm2512454
Deep Learning-Based Carotid Plaque Ultrasound Image Detection and Classification Study
Abstract
Background: This study aimed to develop and evaluate the detection and classification performance of different deep learning models on carotid plaque ultrasound images to achieve efficient and precise ultrasound screening for carotid atherosclerotic plaques.
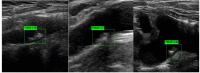
Methods: This study collected 5611 carotid ultrasound images from 3683 patients from four hospitals between September 17, 2020, and December 17, 2022. By cropping redundant information from the images and annotating them using professional physicians, the dataset was divided into a training set (3927 images) and a test set (1684 images). Four deep learning models, You Only Look Once Version 7 (YOLO V7) and Faster Region-Based Convolutional Neural Network (Faster RCNN) were employed for image detection and classification to distinguish between vulnerable and stable carotid plaques. Model performance was evaluated using accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, F1 score, and area under curve (AUC), with p < 0.05 indicating a statistically significant difference.
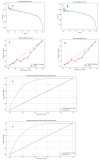
Results: We constructed and compared deep learning models based on different network architectures. In the test set, the Faster RCNN (ResNet 50) model exhibited the best classification performance (accuracy (ACC) = 0.88, sensitivity (SEN) = 0.94, specificity (SPE) = 0.71, AUC = 0.91), significantly outperforming the other models. The results suggest that deep learning technology has significant potential for application in detecting and classifying carotid plaque ultrasound images.
Conclusions: The Faster RCNN (ResNet 50) model demonstrated high accuracy and reliability in classifying carotid atherosclerotic plaques, with diagnostic capabilities approaching that of intermediate-level physicians. It has the potential to enhance the diagnostic abilities of primary-level ultrasound physicians and assist in formulating more effective strategies for preventing ischemic stroke.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; carotid plaque; deep learning techniques; ischemic stroke; vulnerability.
Copyright: © 2024 The Author(s). Published by IMR Press.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Kats L, Vered M, Zlotogorski-Hurvitz A, Harpaz I. Atherosclerotic carotid plaque on panoramic radiographs: neural network detection. International Journal of Computerized Dentistry . 2019;22:163–169. - PubMed
-
- Jain PK, Dubey A, Saba L, Khanna NN, Laird JR, Nicolaides A, et al. Attention-Based UNet Deep Learning Model for Plaque Segmentation in Carotid Ultrasound for Stroke Risk Stratification: An Artificial Intelligence Paradigm. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease . 2022;9:326. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhou R, Azarpazhooh MR, Spence JD, Hashemi S, Ma W, Cheng X, et al. Deep Learning-Based Carotid Plaque Segmentation from B-Mode Ultrasound Images. Ultrasound in Medicine & Biology . 2021;47:2723–2733. - PubMed
-
- Gago L, Vila MDM, Grau M, Remeseiro B, Igual L. An end-to-end framework for intima media measurement and atherosclerotic plaque detection in the carotid artery. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine . 2022;223:106954. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

